By Hayley Munguia, FiveThirtyEight.com
When Samuel Henry was a kid growing up in D.C. in the late 1950s, he and his friends were devoted Washington Redskins fans — they had the jerseys and knew the lore. And as the lore had it, the “reddish-brown tint” of paint on the team’s downtown D.C. headquarters came from the blood of Native Americans. “When I was a kid, me and my friends, we really thought that they had captured and killed Native Americans and pasted them all over the building,” Henry said. “We were just kids, we didn’t know any better. But we really, honestly believed that.”
Now, almost 60 years later, the Redskins are enmeshed in a debate about whether their name is a racist epithet and should be changed. Advocates for keeping the name reference its origins: In 1937, owner George Preston Marshall changed the team name from the Braves to the Redskins. Marshall said the change was in honor of the head coach at the time, William Henry Dietz, who claimed to be part Sioux (although that claim is suspect). Critics including Henry say its origins are irrelevant and that the name is racist and demeaning. “I’d love to see a boycott of all things Redskins,” he said.
Dan Snyder, the current owner, purchased the team in 1999, when it was fighting its first legal battle over the name. The lawsuits have continued, and earlier this year, the Trademark Trials and Appeal Board canceled the franchise trademark because “a substantial composite of Native Americans found the term Redskins to be disparaging.” Snyder has faced mounting pressure to change the name, even from President Obama and George Preston Marshall’s granddaughter. But Snyder plans to appeal the trademark decision and says he will “NEVER” change the name. Polling suggests Snyder has the backing to ignore the calls; most NFL fans (and Redskins fans in particular) oppose a name change.
What’s considered an outrage in the NFL is embraced or at least tolerated all over the country. While we’ve been consumed by the debate about the Washington Redskins, we’ve overlooked thousands of team names and mascots depicting Native Americans, often stereotypically. These teams are not feeling the kind of pressure that Snyder is. To understand the Washington Redskins, we have to understand the Estelline Redmen, the Natick Redmen, and the Molalla Indians, too.
Terry Borning, the proprietor of MascotDB, has kept a database of the nation’s mascots since 2006. He gathers his data from a variety of sources, including state high school athletic associations, websites and local newspapers. Borning’s database doesn’t have every high school, college and pro team in the country, but it does have 42,624 of them. Looking at MascotDB is as close as we can get to understanding how prevalent Native American team names and mascots are across the country.
“There were a lot of interesting mascots where I lived growing up,” Borning said. “But those have mostly fallen by the wayside. Some of those things of the past were definitely offensive, but also more interesting than the generic mascots we have now.”
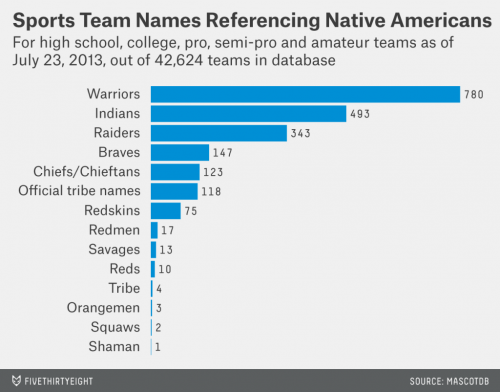
I searched the database and found 2,129 sports teams that reference Braves, Chiefs, Indians, Orangemen, Raiders, Redmen, Reds, Redskins, Savages, Squaws, Tribe and Warriors, as well as tribe names such as Apaches, Arapahoe, Aztecs, Cherokees, Chickasaws, Chinooks, Chippewas, Choctaws, Comanches, Eskimos, Mohawks, Mohicans, Seminoles, Sioux and Utes. (Not all teams with the names “Raiders” and “Warriors” are referencing Native Americans, but we spot-checked 20 schools with each name and a majority of each did.)
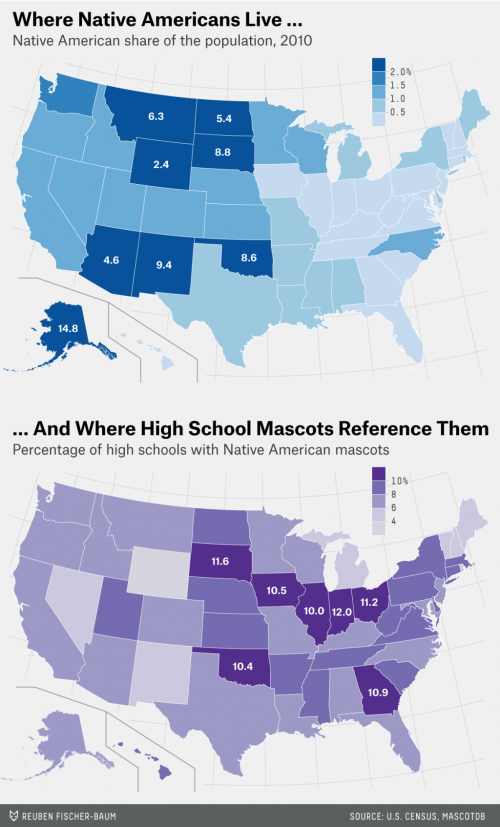
Some 92 percent of those 2,129 team names belong to high schools (the rest were college, semi-pro, pro and amateur league teams). Of all the active high schools in the database, 8.2 percent have Native American team names.
I reached out to about a dozen of those high schools, and most didn’t want to comment on a controversy that hadn’t yet arrived. But the conversations I did have suggested that the way communities regard their teams’ Native American names and mascots depends on the makeup of the communities themselves.
Estelline High, home of the Redmen, is located in a small town in South Dakota, 24 miles west of the Minnesota border. South Dakota has the third-largest Native American population share in the country, but Estelline hasn’t seen the kinds of protests directed at the Washington Redskins. The town has experienced little, if any, controversy over the Redmen name.
The mascot dates back to sometime between 1915 and 1920, when a local newspaper referred to the Estelline athletic team by the color of its uniforms — “the men in red.” The name wasn’t officially adopted, but the team soon became known by its unofficial moniker, the Redmen. According to Estelline superintendent and high school principal Patrick Kraning, the association with Native Americans didn’t come until around 1930. Estelline followed with its own depiction of a “Redman” as a stereotype of a Native American chief wearing a headdress. Events such as the annual naming of a “Moon Princess” and “Big Chief” at homecoming became part of the tradition.
“There’s been very little controversy over the team name,” Kraning said. “In the ’90s there was some discussion about changing the name for a series of schools [throughout southeastern South Dakota] that still referred to themselves as ‘Redmen.’ But in the end, a lot of us — Estelline included — decided to keep the name and just keep away from any Native American imagery associated with it.”
Since then, the only symbol associated with the Estelline Redmen is a logo of an E with two feathers attached. Kraning believes that this change, combined with the fact that Estelline doesn’t have a significant Native American population, is why there hasn’t been much local debate on the topic.
“There’s a community feeling that since the origin of the nickname was not a Native American reference, there’s not a desire for change,” he said. “If there were a discussion, most people would probably view it as going against 80 or 90 years of tradition.”
Natick, Massachusetts, did go against tradition. In 2007, the school board dropped its high school mascot — also the “Redmen” — after an alumna of Native American descent came to the board and said she was offended by the activities surrounding the team she had experienced at Natick High School. The historian for the local Nipmuc tribe told me that the logo and mascot used by the school depicted a “stereotypical northern Native with a headdress,” but that depiction bore no resemblance to the actual indigenous people who lived in the Natick area. Nevertheless, protest groups soon sprouted up, claiming that the Natick Redmen honored Native Americans and were an important tradition.
Soon after the change, school board meetings and a town-wide referendum turned the issue into a much broader discussion. The main critique came from the Redmen Forever Committee, a self-described grassroots effort that sought to influence the non-binding referendum. “We added a question to the referendum asking if townspeople wanted the Redmen name restored,” said Erich Thalheimer, co-founder of the Redmen Forever Committee. “It won overwhelmingly, but the school committee didn’t abide by the town’s wishes.”
“If it were decided by popular vote, we would have the name,” said Anne Blanchard, a member of the Natick School Board. “But we had to take into account our nondiscrimination policy, as well as minority and majority interests.”
The Redmen Forever Committee says it won’t give up the fight. “We chose the name of our committee very intentionally, very purposefully,” Thalheimer said. “This is our town. We’re going to live here until we die. We will forever try to re-establish the Redmen name.”
While the controversy in Natick stemmed from a decision that affected one school, several states have taken a grievance from a single school and used it to forbid Native American mascots. One of the more sweeping bans so far was implemented with the help of Samuel Henry, the man who grew up earnestly believing that the Washington Redskins had painted their downtown D.C. headquarters with the blood of Native Americans. Henry is currently the chair of Oregon’s Board of Education, which instituted a statewide ban on Native American mascots and team names in 2012.
The story goes back to 2006, when Che Butler, a member of the Siletz tribe and a student at Taft High School, raised the issue before the board. Butler said he was offended by the stereotypical and inauthentic manner in which the mascot of a rival school, the Molalla Indians, portrayed Native Americans. He and fellow Taft student Luhui Whitebear, a member of the Coastal Band of the Chumash Tribe, made a presentation at a board meeting asking for a statewide ban on mascots that “misrepresent” Native people, who instead “should be represented with true honor and respect.”
According to Henry, the board agreed that “having Native American mascots did not seem like a good idea,” but decided to defer the decision.
The grievance was taken up again six years later, when the director of public instruction decided to put it back on the board’s agenda. This time around, after some member turnover, the board agreed to ask its chief attorney to draft a proposal for a ban on the use of Native American mascots in public schools. The only dissenting vote came from a woman who claimed that it was too selective, and that devils and saints should be banned as well.
As in Natick, one of the major arguments against the ban came from people who said that the mascots didn’t disparage Native Americans, but honored them. Many of these opponents knew little of Native American culture, Henry said. “I asked one of the students who made that argument what the name of the local Native American tribe was, and she didn’t know,” he said. “To me, that indicated that her reliance on saying that they were honoring Native Americans — that the support for that argument was pretty thin at best.”
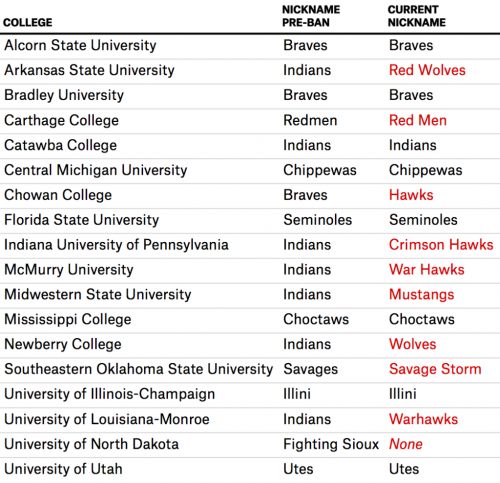
For high schools, a statewide ban is about as sweeping as it gets. Graduate to the next level, though, and schools have broader authorities to answer to. In 2005, the NCAA implemented its own de facto ban1 on Native American mascots for all NCAA colleges.2 The ban focused on a specific list of schools whose mascots were deemed “hostile or abusive,” and precluded them from participating in postseason play if those nicknames or mascots appeared on any team uniforms or clothing.
The NCAA had already taken a stand on a similar issue: the use of Confederate flags. In 2001, the organization banned arenas in South Carolina and Mississippi from hosting postseason championships because the Confederate flag flew proudly on their statehouse grounds. After that decision, the president of St. Cloud State University in Minnesota asked the NCAA to impose a ban on Native American mascots.
The NCAA called on 18 schools (out of 1,046 total member schools at the time, or 1.7 percent) to drop their mascots.
Not all of the targeted schools felt that their nicknames or mascots were “hostile or abusive,” and the ban was followed by a surge of criticism.
“I must have gotten 2,000 emails from people just complaining about it,” the NCAA’s executive committee chairperson at the time, Walter Harrison, said. Even almost 10 years later, he still remembers one persistent caller. “He, or she, I don’t know if it was a man or a woman, would call my office phone at four in the morning and just play their school’s chant until the answering machine cut off,” he said.
But the more serious backlash came in the form of appeals. One came from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and its Fighting Illini. The Fighting Illini were portrayed at halftime performances by a student dressed in full Lakota regalia, including face paint and a headdress. He went by the name “Chief Illiniwek,” and became the focus of the university’s fight against the ban.
Controversy surrounding Chief Illiniwek predated the NCAA’s ruling by decades. The university’s board of trustees had been quietly in the process of considering a potential mascot change since 2001, and the publicity surrounding the nationwide ban reignited already-existing tension among students and alumni. Lawrence Eppley, who was the chair of the university’s board of trustees at the time, said he received hundreds of comments from foundations and alumni organizations threatening to withhold donations. He and the rest of the board figured the only option was to strike a compromise to keep both sides — passionate students and alumni and the NCAA — happy.
Through its appeal, the school was allowed to keep its team name, but not its mascot. Chief Illiniwek portrayers, who had been a part of an official student organization called the Council of Chiefs, could continue the tradition as long as the group no longer had any official affiliation with the university. “One of the things that made it tough to retire it was making sure the fans knew that, if you loved the chief, that was nothing to feel guilty about,” Eppley said. “It’s just that times change, and there’s not much we can do about that.”
Ivan Dozier, who currently portrays Chief Illiniwek, said that officially retiring the mascot was the wrong way for the university to respond. He believes that Native American mascots are a way to reach and educate an audience that wouldn’t normally be knowledgeable about Native American culture or history. “What concerns me is if you eliminate all references to Native American culture, people aren’t asking questions anymore,” he said. “Sports fans here are the vocal majority. They’re the ones who need this information the most, and now they have no way to go about getting it.”
Eight of the schools on the NCAA’s list secured vocal support from local Native American tribes to successfully appeal and retain their team names and mascots. Eight others have changed their names and one dropped the use of a mascot entirely. Carthage College changed its team name from the Redmen to the Red Men and dropped all Native American imagery, which satisfied the NCAA’s requirements.
Turning the Washington Redskins into the Red Skins is unlikely to appease the team’s critics, though. Given that the name is racist by definition and no tribe has come out in support of Snyder, it probably wouldn’t pass the NCAA’s grounds for appeal, and it certainly doesn’t pass in the court of Native American opinion.
But even if the Redskins became the Red Skins or the Red Flyers or the Red Snyders, there would still be thousands of other teams that reference Native American imagery. Whatever happens with the Redskins, there will still be the Estelline Redmen, Chief Illiniwek, and the West Texas Comanches, each upholding the questionable legacy of Native American sports names.