By Michael Collier California Magazine
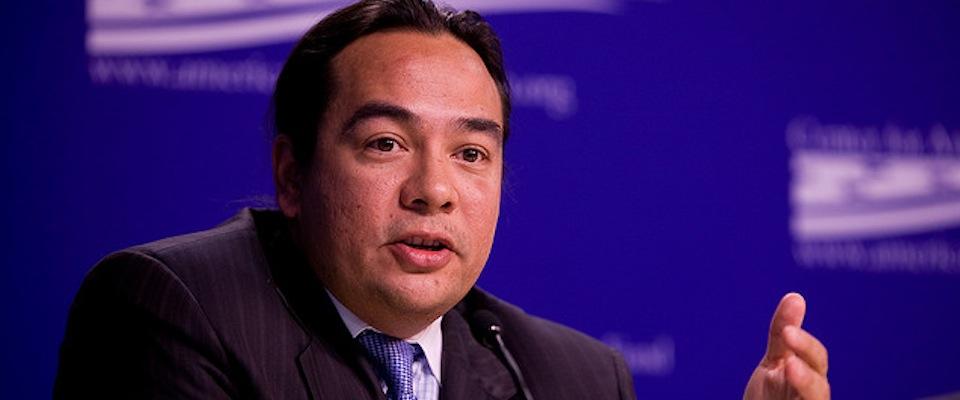 Keith Harper says he always wanted a career that helped his people—indigenous people.
Keith Harper says he always wanted a career that helped his people—indigenous people.
Harper’s dream, which he cultivated while a student at UC Berkeley, was more fully realized this week when he became the first Native American of a federally recognized tribe to earn the post of U.S. Ambassador. This week, he begins his new job as the U.S. representative on the United Nation’s Human Rights Council, which is meeting in Geneva, Switzerland.
As a young man, Harper attended UC Berkeley, where he graduated in 1990 with a bachelor’s degree in sociology and psychology. He would later return to Cal to address a group of Native American students, says Bridget Neconie, Native American Outreach Adviser in the undergraduate admissions office.
Having completed law school at New York University in 1994, Harper became an attorney and began to make his dream come true. A member of the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, he helped represent a half-million Native Americans who claimed in a class-action lawsuit in 1996 that the federal government, which had held their families’ land in trust for a century or more, had failed in its fiduciary duties.
More than a decade later, he was part of a legal team that helped secure a $3.4 billion settlement in the landmark case, which was approved by a federal judge in 2011.
The U.S. Senate, in a 52-42 vote last week divided along party lines, confirmed Harper for the post of U.S. ambassador, with support from California Senators Barbara Boxer and Dianne Feinstein.
“Ambassador Harper is well-qualified for this position and he had strong backing, including from within Indian country,” Sen. Barbara Boxer said in a statement Wednesday. “I was proud to support his nomination as the first U.S. Ambassador from a federally recognized tribe.”
Tribal leaders across the nation also praised Harper for winning the post. “Ambassador Harper is an attorney who has dedicated his career to the injustices facing Native peoples,” leaders of the National Congress of American Indians said in a statement. “Issues surrounding Indigenous peoples have emerged prominently on the agenda of the United Nations, and Ambassador Harper will be a valuable resource to the Human Rights Council.”
Some Senate Republicans refused to back his confirmation because of his involvement in the class-action case and for being a major campaign fundraiser, known as a bundler, for President Obama’s 2012 re-election campaign. Harper brought in more than $500,000 for the campaign.
“Mr. Harper is just another example of a campaign bundler wholly ill-suited to serve in the diplomatic post for which he’s been nominated,” said Sen. John McCain, R-Ariz. McCain added that Harper and his legal team received excessive attorneys’ fees in the class-action case—also a point of contention among some tribal leaders. Harper’s firm and two solo practitioners earned nearly $86 million in attorneys’ fees, according to court documents cited by the Washington Post.
At a news conference in Geneva on Monday, Harper said he will represent oppressed people around the globe and will support the work of non-government organizations that promote human rights. “In our work here, we must never forget our duty to champion the rights of the most vulnerable and to speak for those who have no voice,” Harper told reporters. “Whether those champions are in the media or are those from civil society or human rights defenders, the United States will continue to stand with you.”
With backing from the United States, Harper said, the Human Rights Council, established in 2006, has put a spotlight on human rights issues in Syria, North Korea, Iran and the Central African Republic.
In a 2007 interview posted on the website of New York University’s law school, Harper talked about his mission to serve Native Americans. “ I decided to work in Indian Law,” he said, “because I strongly believe that the law can be utilized to achieve real benefit for our tribal communities through securing their common rights and protecting our lands and way of life.” He added that the landmark case, Cobell v. Kempthorne, was “mostly about one woman, Elouise Cobell, saying enough is enough—a trustee needs to be accountable and is not the boss but a servant….” The settlement included $1.5 billion in payouts to the 500,000 members of the class action; a $1.9 billion program to consolidate land to help tribes benefit from agriculture, business and housing development; and a $60 million scholarship fund.
The most rewarding part of his career, he said, “is working with American Indian people. There is nothing better for me than to meet with Native clients and figure out ways to solve the problems they confront. Indian people are poised for greatness and I feel very fortunate to be able to be part of the machinery that will permit us to achieve that.”



 An excerpt from the complaint, still being refined into its final, legal form, reads: “This letter serves notice as complaint, that the crime of genocide is being committed, in an ongoing manner, against the matriarchal Tetuwan Lakota Oyate of the Oceti Sakowin, an Indigenous First Nation people whose ancestral lands comprise a large area of the Northern Great Plains of Turtle Island, the continent known as North America.” As evidence, the Lakota cite systematic American usurpation of their land and sovereignty rights, imposition of third world living conditions on the majority of Lakota, US assimilation policies that threaten the future of their language, culture and identity, and environmental depredations including abandoned open uranium mines and the proposed Keystone XL Pipeline slated to invade the Pine Ridge Reservation. The Lakota grandmothers and their allies in the Lakota Solidarity Project have even produced a powerful, full-length documentary, Red Cry, available on DVD or online at
An excerpt from the complaint, still being refined into its final, legal form, reads: “This letter serves notice as complaint, that the crime of genocide is being committed, in an ongoing manner, against the matriarchal Tetuwan Lakota Oyate of the Oceti Sakowin, an Indigenous First Nation people whose ancestral lands comprise a large area of the Northern Great Plains of Turtle Island, the continent known as North America.” As evidence, the Lakota cite systematic American usurpation of their land and sovereignty rights, imposition of third world living conditions on the majority of Lakota, US assimilation policies that threaten the future of their language, culture and identity, and environmental depredations including abandoned open uranium mines and the proposed Keystone XL Pipeline slated to invade the Pine Ridge Reservation. The Lakota grandmothers and their allies in the Lakota Solidarity Project have even produced a powerful, full-length documentary, Red Cry, available on DVD or online at 


