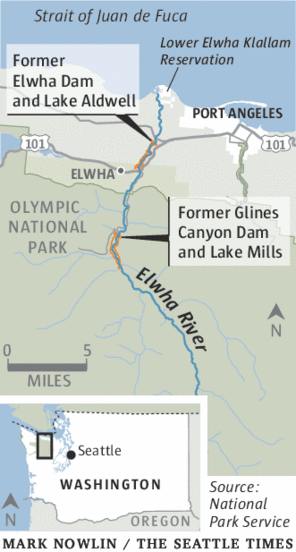
What’s left of the 210-foot-high Glines Canyon Dam, a section of about 30 feet, is awaiting a final blast in September. In the distance, the bottom of former Lake Mills today forms part of the new Elwha Valley.
Fish are storming back to the Elwha, there’s a sandy beach at the mouth of the river again, and native plants are growing where there used to be lakes.
By: Lynda V. Mapes, Seattle Times
The last dam will be blasted out of the Elwha River sometime next month, cementing the hopes of generations of advocates and tribal leaders who fought to make it happen.
With the concrete out, the long-term revival of a legendary wilderness valley in the Olympics can now unfold unfettered after 100 years dammed.
The watershed already is springing back to life from the mountains to the sea: Salmon are swimming and spawning miles above the former Elwha dam site. Alders stand more than head high as the native forest reclaims the former lake beds. There’s a soft, sandy beach at the river mouth, where before there was only bare cobble. And birds, bugs and mammals are feasting on salmon eggs and carcasses as fish once again nourish the watershed.
The Elwha is a rare chance to start over on a grand scale. The $325 million federal project, begun three years ago, has reopened 70 miles of habitat for steelhead and salmon, rebuilt wildlife populations and restored native plants. The river is hard at work with its restored natural flow, rebuilding its plunge pools, log jams and gravel bars.
While it will never be the Eden it was, the Elwha one day likely will be pretty darn close — and sooner than many expected.
“It goes against my deepest notions of how fast ecosystem recovery can possibly happen,” said Christopher Tonra, a research fellow with the Smithsonian Migratory Bird Center in Washington, D.C., who is tracking the response of dippers, a native, aquatic songbird, to dam removal in the Elwha. “We are all trained, as biologists, to think of things over the long run. I am not saying the Elwha is fully recovered. But it is so mind blowing to me, the numbers of fish, and seeing the birds respond immediately to the salmon being there. It makes the hairs on the back of my neck stand up.”
Early hydropower
The dams were built beginning in 1910 for hydropower, but lacked fish passage. It took an act of Congress, passed in 1992, to finally take down Elwha Dam and then Glines Canyon Dam, about eight miles above it.
Unbuild it, and they will come: Salmon have been storming back ever since Elwha Dam was blasted out of the way in March 2012. Taking down Glines Canyon Dam has taken longer, in part because it holds back a larger load of sediment.
Managing the release of about 27 million cubic yards of sediment as the dams come down is why removal has taken so long. There was so much sediment stuck behind the former Glines Canyon Dam alone that, stacked up, the pile would tower more than twice the height of the Empire State Building, notes Jonathan Warrick, of the U.S. Geological Survey.
The dams were lowered notch by notch, allowing the river to naturally flush about half the total sediment load downriver and out to the Strait of Juan de Fuca.
There have been bumps along the way. A water-treatment plant — the single most expensive part of the project — failed when a critical intake clogged with debris rinsed out by the river, delaying removal by a year while repairs were made.
The tribal hatchery and federal fish-restoration plan, which includes stocking of some hatchery fish, have been a magnet for lawsuits and controversy.
But nature, meanwhile, has carried right on.
Ian Miller, a coastal hazard specialist based in Port Angeles for Washington Sea Grant, has been monitoring the beach at the river mouth.
The surprise to him isn’t the big volume of sediment the Elwha is delivering downstream, but the fact that it is sticking around. “Basically, this is all new land,” Miller said, walking the beach east of the river mouth on a recent visit. “Everything here is less than two years old. You can walk to (sandy) spots on the beach that are 30 feet deep. It is just a dramatically different system.”
A beach that used to be too rocky to comfortably walk on is today used by kids to play soccer.
Meanwhile, fat chinook salmon are cruising up the river. Staff from the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife started working the Elwha in July with a gill net to eventually capture 1,600 big Elwha fall chinook. The fish, of both wild and hatchery origin, are taken to stock the next generation of Elwha fall chinook raised in the state rearing channel, used since the 1970s to preserve the unique Elwha strain.
Stars of the river
Working the fast current was a fish rodeo to capture, then quickly take the powerful, thrashing fish from the net unharmed. Long and thick as a thigh, the chinook, the largest in the Puget Sound region, are the celebrities of Elwha River restoration, and a major reason for dam removal.
Elwha fish populations are projected to grow from about 4,000 to 400,000 over the next 20 to 30 years. Salmon already have hatched and migrated up- and downstream of the former Elwha dam site for the first time in a century.
Revegetation — the most visible piece of the Elwha renewal project — also is unfolding dramatically. Already, terraced banks of the former lakes are burgeoning with alder and cottonwood, the gift of seeds carried by the lakes as they gradually were lowered during the drawdown that started dam removal.
Most difficult to revegetate are the cobbly, gravel flats of the lake bed farther upstream, in the former Lake Mills, a land where many a planted Douglas fir and other seedlings have gone to die.
But in other spots, cottonwood seedlings have established so thickly they look like a lawn. Alder trees seeded in 2011 as lake levels dropped now have grown more than head tall. Where there used to be bald sand, goldenrod buzzes with bees, and a young, stocky Nootka rose bush conceals a bird’s nest full of eggs.
In all, more than 500 acres of former lake bed are being replanted, with nearly 60 varieties of native grasses, flowers, woody shrubs and trees from the Elwha Valley through 2018.
Dam removal also is kick-starting broader effects in the ecological systems of the watershed, from its food chain to the home ranges of animals.
Kim Sager-Fradkin, wildlife biologist for the Lower Elwha Klallam Tribe, already has tracked fish-eating otters to parts of the Elwha that salmon have recolonized since dam removal, and documented an increase in the otters’ nutrient levels derived from fish.
John McMillan, a biologist with National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Fisheries walking the tributaries since dam removal began, said that in the first year he saw salmon carcasses on the riverbank. But now he doesn’t because the otters, bears, cougars, bobcats and mink have learned to take advantage of food where for so many years there was none.
“The ecological relationships between the animals are coming back,” McMillan said. To me, that is such a great feeling.”
Walk the river
Take a walking tour of the Elwha River with Park Service rangers on the former Lake Aldwell. Tours are on Tuesdays and Sundays at 1 p.m. through Sept. 2. The hourlong walks are free, and begin at the former boat launch at the end of Lake Aldwell Road, north off of Highway 101 just west of the Elwha River Bridge. For more information, call 360-565-3130.