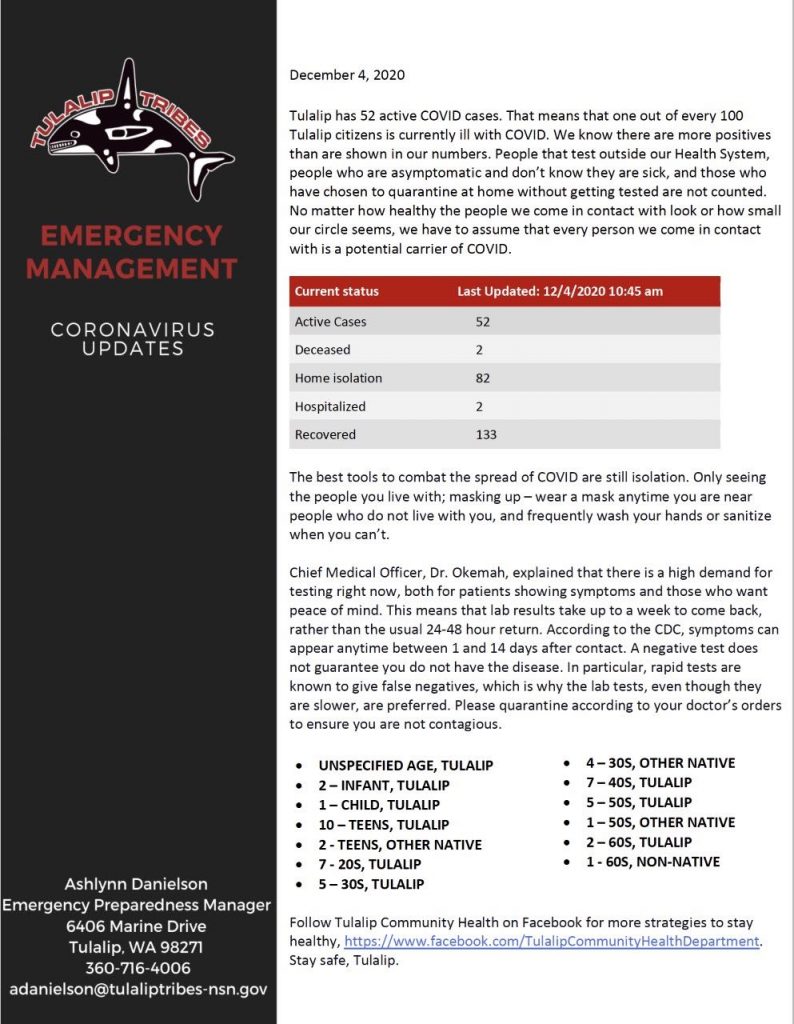
Emergency Management Coronavirus Update, Dec 4, 2020

syəcəb

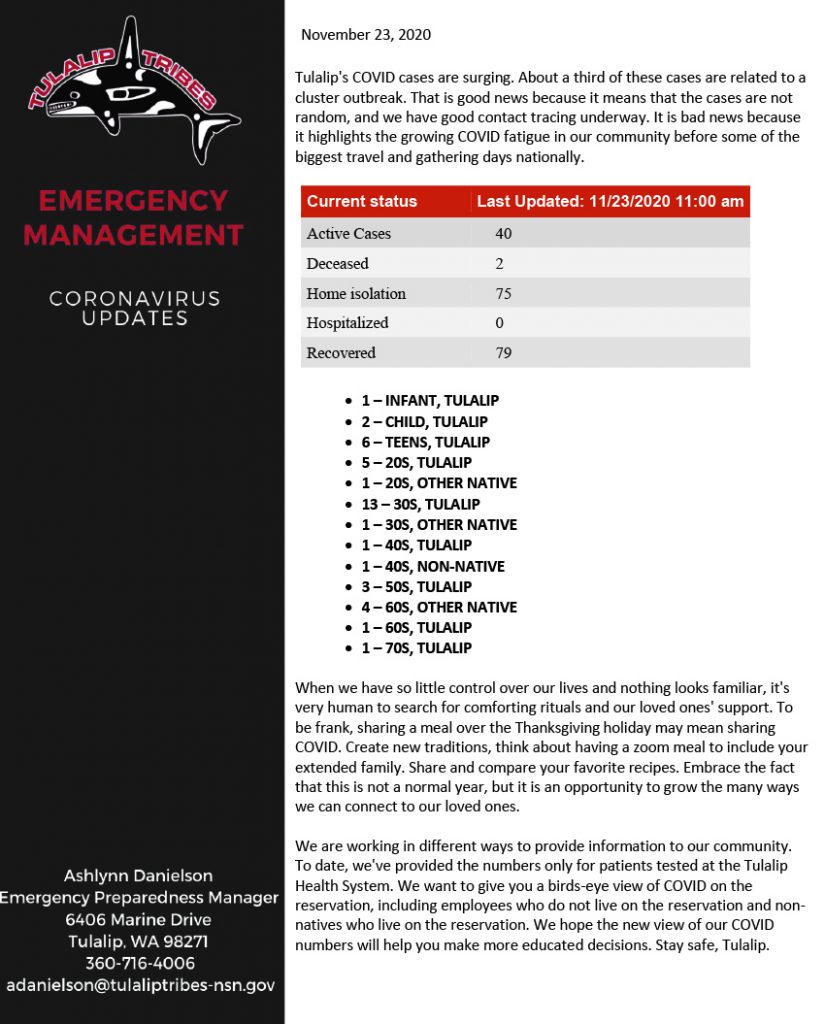

By Kalvin Valdillez, Tulalip News
Did you know that there is a program that helps with resources, education, and general support designed specifically for Tulalip tribal families living with children? If not, you’re not alone as the program is still relatively new. A division of beda?chelh, the young program is spreading the word about their services and what they can offer Tribal families.
Stated beda?chelh manager, Natasha Fryberg, “I want to bring forth our FIT team to start getting more resources out in the community so we can create positive engagement with potential clients and families.”
The Family Intervention Team, or FIT, currently consists of two social workers, Lena Hoeflich and Kayleigh Canby, who are dedicated to aiding Tulalip families by helping them along their journey through tough times. Whether you are a single pregnant mother or a family dealing with a rebellious teen, they are available and ready to help support you and provide any services or needs you may require.
“I always describe it to clients as a voluntary program,” said Kayleigh. “Our goal is to kind of bolster the family, or bring in supports, to help them be successful in whatever they want to do. Usually, the goal is to try and keep their families together and we bring in those supports to help them be successful. We support parents, we support children, we support everybody.”
The FIT mission is to achieve immediate and lasting positive change for families, in the best interest of the children, whether you live on or off the reservation. FIT makes it their priority to see that you receive assistance and will refer you to a program, professional or specialist who will provide you with further care.
Lena explains, “We try to bridge a gap that a family might be experiencing, a hardship – whatever that may be. We meet with families and it is family-led. It’s not prescriptive, because it just depends on whatever the family needs, and whatever they’re going through at that time. For example, if someone calls and says this person was driving and their kid wasn’t in a car seat, we can come in and ask if we can educate them on the necessity of a car seat. Can we provide them with a car seat? We can ask, what else do they need? Do they need groceries? Do they need help paying bills? Do their kids need assistance being set up in online schooling?”
Some resources and services that FIT assists families with include parenting skills, housing, food and nutrition, domestic violence, independent living skills, chemical dependency, teen support and mental health.
“If a family is experiencing a really difficult time with their teenager, we work with them and get them set-up with Family Haven. We will work with them before, during, and after they have those intervention services, just to make sure that everything is continuing to go well. Or we might work with families who may have difficulty paying a bill. We look to see if there are resources within the Tribe or within the state or Snohomish County, just to try to find different ways to help,” said Lena.
Kayleigh added, “I have a mom that I’m working with right now and I’m trying to help her find a mental health counselor. At the same time, I reached out to a couple different agencies locally, she’s a pregnant mom, so she needs a bed to sleep on. We do the legwork of trying to find those materials. I have another family and their children are in need of winter clothes, so we find those resources in the community to get warm clothes for those kids.”
The majority of clients and families that FIT has helped so far are referrals from Child Protective Services. However, FIT wishes to assure Tribal members that they are here for the people, and welcome any community-referred and self-referred clients. Although they are an extension of beda?chelh, their focus is to work with clients and take preventive measures and progressive steps to help keep families together.
“A lot of families have a huge support network, but there are other individuals who don’t have any support networks at all,” Kayleigh expressed. “We’re here to help support them, we are apart from CPS. We are a voluntary program, we’re not going to hunt you down or tell you what to do. I think that’s the biggest message is that we’re just here to help, we’re here to raise-up the community in the ways that they want.”
Lena agreed, saying, “I think that’s a distinction that we’re trying hard to make people understand, because when we do call and say we’re a new program with beda?chelh, that usually closes the door immediately. We’re very different. The whole point of our program is to prevent families from having interventions or any interaction, really, with CPS or the court systems. We’ll work with any family who we think would be a good ‘fit’ in the program.”
For additional information about the Family Intervention Team, please contact (360) 716-3284.


Submitted by AnneCherise Jensen
People from many cultures have a long history of gathering mushrooms for food, medicine, dyes, clothing and decoration. Over the centuries, humans have accumulated a considerable amount of knowledge about mushrooms, whether they be poisonous, edible or medicinal species. However, because of their variety of health effects, many people have steered away from incorporating wild mushrooms and other fungi into their diet.
Mushrooms are a common, and plentiful wild edibles that grows naturally in the Pacific Northwest. If we have the proper tools, hands on experience, education and resources, we can easily identify and locate some edible species and incorporate them into our diet. This article will dive deeper into some common variations of local, edible mushrooms, their health properties, and how to incorporate them into meals in the kitchen. Let’s get started!
Did you know that there are over 2,000 varieties of edible mushrooms? In fact, there are actually more species of edible mushrooms than poisonous mushrooms. Most poisonous mushrooms won’t kill you, side effects usually include upset stomach, vomiting and/or food poisoning symptoms. Some common poisonous mushrooms grown in the PNW include Sulfur Tufts and certain types of Amanitas. Keep in mind, poisonous mushrooms are only harmful when eaten. The harmful toxins they contain cannot penetrate the skin, and won’t harm you if touched, only digested. Make sure to always cross reference a species before consuming.
Edible mushrooms are tasty, nutritious and can be used in a wide variety of dishes. Mushrooms contain the 5th flavor called umami, which is also known as savory and having a meat-like taste and texture. In fact, mushrooms can often be used as a meat substitute in the kitchen. Foraging for local mushrooms is an economical and nutritious way to enhance meals at home (they’re free). There are thousands of nutrient dense mushrooms in the forest just waiting to be eaten. The best part is the more you forage wild mushrooms, the more abundant they grow the following year. Here are some tips to help you on your next mushroom forage.
Mushroom Foraging Tips:
Common species of locally foraged, edible mushrooms:
There are over 100 species of edible mushrooms that are common in the Pacific Northwest region. Some species are rarer and some are generally easier to find. Here are five common wild mushrooms I’ve personally identified and located in our region, starting from most common to least common.
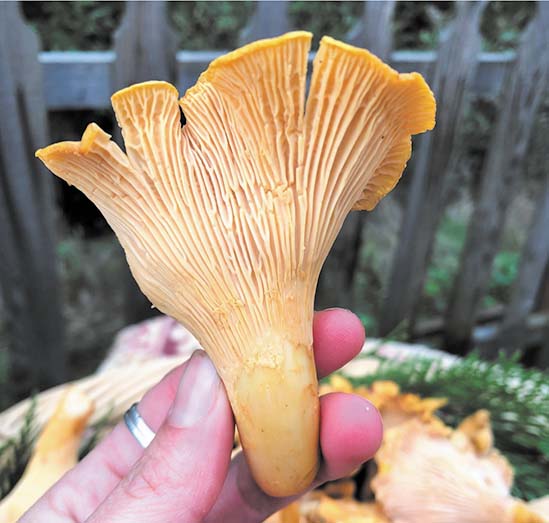

Chanterelles: Chanterelles rank among the most popular edible wild mushrooms. Chanterelles are usually vase or trumpet-shaped mushrooms with wavy-like gills. This mushroom has a fruity, apricot-like aroma and mild, peppery taste. Most are yellow or orange. In its healthiest form, this is a very firm & rigid mushroom, don’t harvest if mushy or gooey.
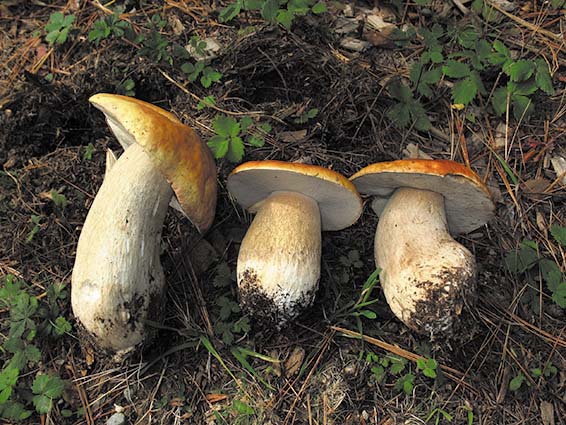

King Bolete: There are about 20 different types of Boletes that grow in the Pacific Northwest. They contain spores underneath their caps, and are usually very spongy. Most Boletes are edible, but vary in flavor. The King Bolete is one of the most common edible Boletes in this region. They are medium to large in size, caps are usually yellow-brown, red-brown, or dark red. This is the largest Bolete and is usually pretty easy to identify.
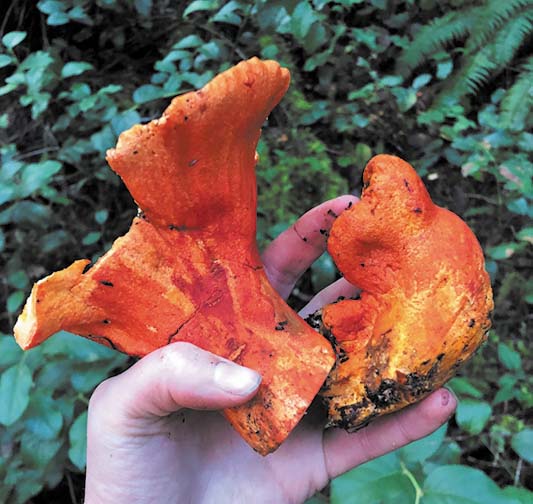

Lobster Mushrooms: Medium to large sized mushroom, in a layer of bright orange to vibrant red tissues, usually shaped like an upside down pyramid. Found in woods, especially under conifer trees in the Pacific Northwest. Lots of flavor and considered a high quality edible. With its unique vibrant red colors, this mushroom is one of the easiest to identify.
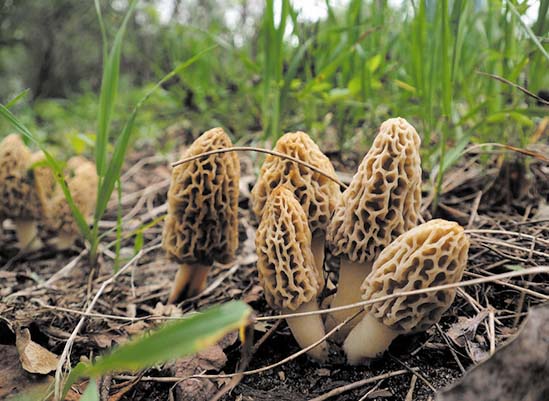

Morel: Morels have a distinctive honeycomb-like shape and vary in color from light yellow to dark brown. They are earthy in flavor and should be cooked before eating. However, these are usually only harvested in the spring months in recent forest burn areas.
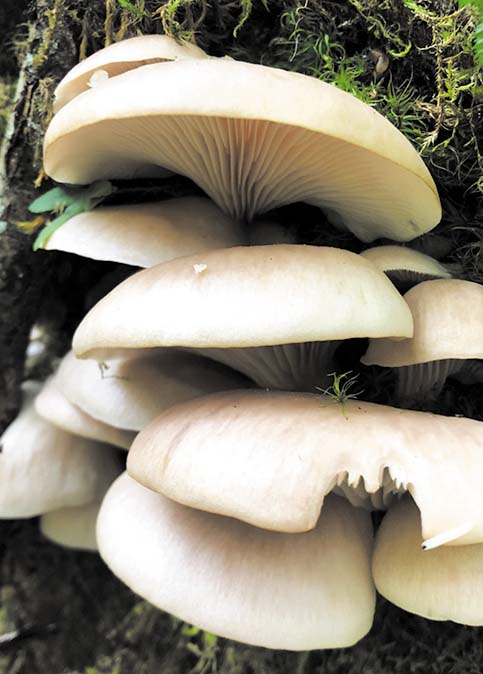

Oyster Mushroom: Oyster mushrooms are usually white, light grey or light yellow. They are smooth, trumpet-shaped that grow in clusters and have a light flavor. There are a few species of oyster mushrooms. All are edible but vary in flavor, color and shape.
Mushroom Identification Resources: Below are some mushroom identification books that I use frequently. There are others out there, but these are just a few that I’ve used. I find it helpful to use books that are specific to your area. Mushrooms of the PNW is probably my most used and helpful book. Check your local bookstore or find these off Amazon.
Nutrition Properties
“One cup of raw sliced mushrooms has approximately 20 calories and are a good source of potassium and, depending on the variety, can provide selenium and copper. Mushrooms have significant amounts of three B-complex vitamins: riboflavin, niacin and pantothenic acid. The B vitamins help release energy from the fat, protein and carbohydrates in food. They also can be excellent sources of vitamin D if they have been exposed to ultraviolet light right before or after harvesting”. (Wolfram)
Cooking & Consuming
Mushrooms provide a wide range of flavors and opportunity in the kitchen. However, when first starting to eat wild edible mushrooms, it’s best to start by eating them in small portions. Some individuals have a hard time digesting wild mushrooms and get a mild upset stomach at first. The best way to overcome this, is to start with small portions and gradually eat more wild mushrooms as you get more comfortable with them. A suggestion to those who pick a mushroom variety for the first time – have an adult cook and taste a small amount of the mushroom first, and wait 24 hours to be sure there is no reaction, before making a large portion to serve to family, especially kids. When cooking, make sure the mushrooms are fully cooked, usually about 10-20 minutes of frying, steaming, sautéing, or baking will cook them thoroughly.
Sources:

By Kalvin Valdillez, Tulalip News
As the original caretakers of this region, the Tulalip people share a deep connection with Mother Earth. Generation after generation, the youth are taught about the natural world; the knowledge of plants and their medicinal components, as well as their use for sustenance and ceremonial purposes, including but not limited to regalia and blessings. The traditions are usually passed on through families. Today, classes are offered by a number of departments and traditional ceremonies are often open to the public, helping pass down that knowledge on a larger scale and ensuring the sduhubš way of life is preserved and lives well into the future of Tulalip lineage.
One such program that develops cultural lessons and projects, and thereby provides the Tulalip people with a deeper understanding of the local Native plants and their many uses, is the Rediscovery Program. Originally started by Tribal members Hank Gobin and Inez Bill, Rediscovery was recently, in traditional fashion, handed off to the next generation as Virginia Jones and Taylor Henry take the knowledge learned, working alongside Inez, and prepare to put a new spin on tradition.
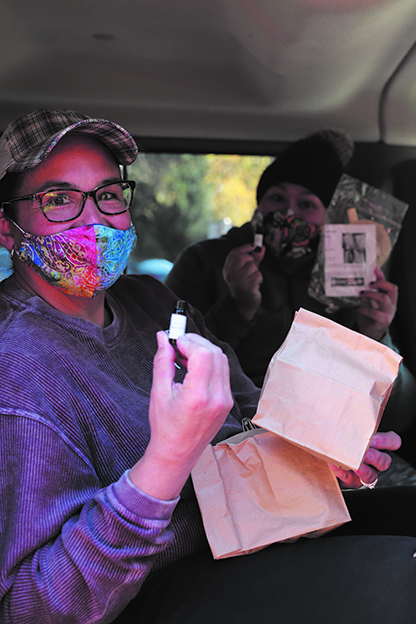

The program has been invested in the annual Tribal Canoe Journey and makes traditional medicinal supplies with the community, not only for the Tulalip Canoe families, but also to gift to the hosting tribes along the way. Throughout the year, the program will hold classes at the Hibulb Cultural Center where tribal members can create handmade products such as lip balm, sunscreen, salves, headache and sinus oil, tea, and also sage and cedar bundles for Journey. With the cancelation of Canoe Journey this year, the Rediscovery had an abundance of product that would expire if not used within the year.
While determining what to do with the handmade goods, the program was met with yet another challenge – how to provide their services to the tribal membership during a worldwide pandemic.
Explained Virginia, “We had to find a way to provide a cultural connection for our people. And when we were thinking about classes, it didn’t feel like that was reasonable around COVID. We were considering how many different family members and households we could reach if we put together this drive-thru kit idea, and we’ve been able to reach a lot more families than if we were just providing classes.”
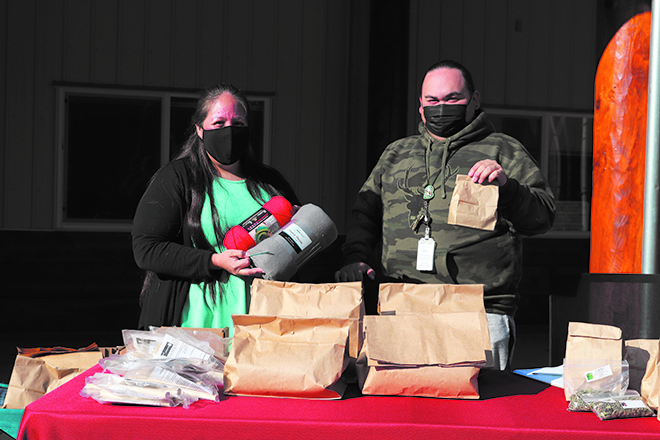
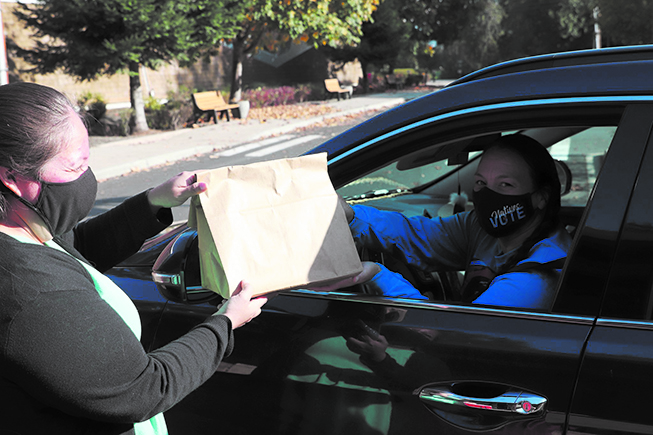
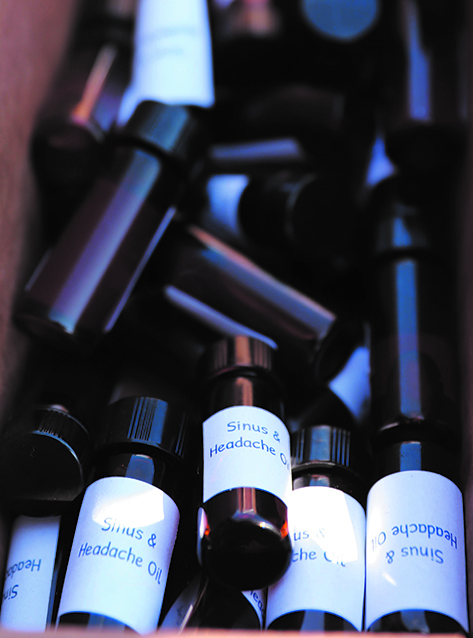
Once-a-month, you can catch the Rediscovery team offering medicine, in the form of both laughter and DIY craft kits, at the far end of the Hibulb Cultural Center parking lot. Since the kits are offered to Tulalip tribal members only, Virginia and Taylor advertised the first two events solely on the Tulalip tribal member Facebook page. Those advertisements alone brought hundreds of people by the carload to see what the program has to offer their families. Each tribal member chooses one kit of their liking and receive one bottle of sinus and headache oil.

“Some of that smudge from Journey are in these kits because we figured that maybe the Tulalip families could use those things even though they were put together with the intention of being for Journey,” Virginia continued. “The sinus and headache oil was another one of the items that people got together to make. With a lot of these plant medicines, it’s better that they get used than waiting until next Journey, so we decided we would provide them to the community.”
On the morning of October 22, Rediscovery set up shop and were busy throughout the day while cars trickled in and out of the Hibulb parking lot. People had three options to choose from; shawl kits complete with thread and needle, rawhide rattle kits or a smudge blend and loose-leaf tea kit. Tribal member Theresa Sheldon expressed that COVID cannot stop the culture when she dropped by to pick up several kits for herself and her nieces to construct while they spend a little family time together.
“I love this, because we are all at home and this really helps,” said Theresa. “I have nieces who we’ve been doing art projects with, so it’s perfect being able to teach them how to do this stuff, because they’re going to carry this on after us. And it doesn’t stop, the teachings and the time to learn, that doesn’t stop as time goes on.”
Overall, 251 DIY kits were handed out during October’s drive-thru event, as well as 261 medicinal plant kits with items such as four thieves room spray, smudge blends, tea and sinus and headache oil. The next drive-thru kit-giveaway will take place on November 4th, beginning at 9:00 a.m. Rediscovery is currently planning drive-thru events through March 2021, but Virginia warns that could change depending on any new developments of the COVID-19 virus.

“I would say that they’re all very happy when they come through to pick up their kits,” assessed Virginia. “It’s hard for them to choose because they want a little bit of everything. I’ve seen a couple people respond to us, showing their completed crafts. We hope to offer different kits at each drive-thru for each month. The November drive-thru will probably be necklace kits – it’ll be a carved paddle or a carved canoe head with string and sandpaper, but they’ll have to do their own beads this time.
“We miss being able to offer the classes and the culture night events in-person. We miss being able to spend time, sharing-in all of those cultural activities, like gathering together and making items. But, we are definitely glad to see the families who come through and take some of these kits home because then at least we know that they can spend that time with their family making those things.”



Submitted by Sydney Gilbert, Forensic Interview Coordinator, Tulalip Children’s Advocacy Center
October is National Domestic Violence (DV) Awareness Month. This year with the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s more important now than ever that we learn to recognize the signs and symptoms of DV as it often thrives in the secrecy and silence of the home. Many people are staying home to stay safe from the pandemic. But for the 84% of Native people who have experience violence in their lives, home is not always a safe place to be (Rosay, 2016).
According to the Rosay study, more than 56 % of Native women had experienced sexual violence and more than 55% had experienced intimate partner violence in their lifetime. 27% of Native men had experienced sexual violence and over 43% had experienced intimate partner violence in their lifetime. According to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, “Intimate Partner Violence describes physical violence, sexual violence, stalking, or psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse. This type of violence can occur among heterosexual or same-sex couples and does not require sexual intimacy”.
It important that we understand the high rates of violence against Native Americans. Strong Hearts Native Helpline reminds us that “the parallels that can be drawn between colonialism and domestic violence can be seen through their definitions and through a review of Native American history. Having lived through genocide and horrific suffering, the aftermath of European contact and colonization continues to not only haunt Native Americans, it wreaks havoc in their everyday lives” (Strong Hearts Native Helpline, 2017). This is likely why 84% of Native women and 81% of Native men have experienced sexual violence, intimate partner violence, stalking, and/or psychological aggression by an intimate partner in their lifetime. (Rosay, 2016).
One thing we can do as a community to combat DV is to be open to talking about and learning about it. If we want to end intimate partner violence we need to be willing to stop thinking of it as a “family issue” that is to be kept quiet. Common signs of abusive behavior in a partner include:
Tulalip Tribes Legacy of Healing is here to listen and help in any way we can. If you’re experiencing DV or know someone who is and want resources on how to help, Legacy of Healing is here for you. Our mission is to promote a safe, healthy, and non-violent community for non-offending tribal members and their families by providing education, survivor advocacy, and accountability through a coordinated community response. Our services include civil and legal advocacy for adult victims of domestic violence, sexual assault, dating violence and stalking, outreach, and education.
Legacy of Healing is located at 7720 Waterworks Road in Tulalip. We are open Monday-Friday 8:00-4:30. Call us at 360-716-4100 or email at loh@tulaliptribes-nsn.gov. Please scan our QR code and “like” our Facebook page for additional trainings and resources.

If you are in crisis you can also call the National Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-7233. Strong Hearts Native Helpline can be reached at 1-844-762-8483.
References:
Center for Disease Control. (2018, October 23). Intimate Partner Violence. Retrieved October 7, 2020 from https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/intimatepartnerviolence/index.html
Rosay, André B., “Violence Against American Indian and Alaska Native Women and Men,” NIJ Journal 277 (2016): 38-45, available at http://nij.gov/journals/277/Pages/violence-againstamerican-indians-alaska-natives.aspx.
Strong Hearts Native Helpline. (2017). Domestic Violence in Indian Country and Alaska. Retrieved October 7, 2020 from https://www.strongheartshelpline.org/domestic-violence-in-indian-country-and-alaska/