
The Moms Group is now online

syəcəb

Please use the following link to download the August 8, 2020 issue of the syəcəb

Submitted by Lindsey Watkins, Marketing Manager, Tulalip Tribes
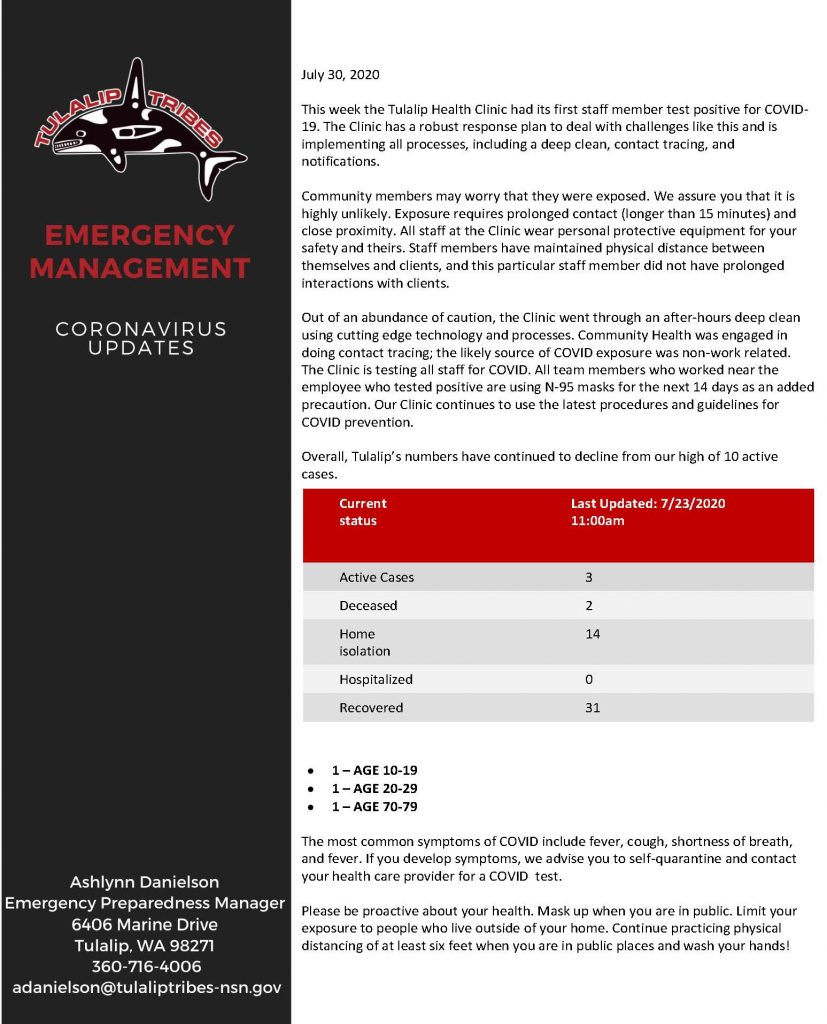
Beginning August 10, if you have not completed your census survey, a census enumerator will visit your home to ensure that you and your family are counted. Census enumerators are your neighbors–people from your community, hired by the Census Bureau, to go door-to-door and collect census information from residents that have not completed their 2020 Census. Census enumerators can be identified by ID cards displayed openly, their official Census bag, and are likely members of your community, so welcome them when they arrive—the whole process should not take more than 10 minutes. The census taker or field representative will present an ID badge that includes their name, their photograph, a Department of Commerce watermark, and the expiration date. They will have an official bag and Census Bureau-issued electronic device, such as a laptop or smartphone, bearing the Census Bureau logo. Census takers and field representatives will conduct their work between the hours of 9 am and 9 pm.
If a census enumerator comes to your door, they will interview you so they can count all the residents of each household. They will ask you approximately ten questions on their electronic form and fill in your answers. Even if you just forgot to complete your form, the census taker still must ask you the questions and complete the form with your answers. They cannot let you fill out their form for them. They will be wearing a face mask and staying outside your door following CDC guidelines and not ask to come into your home.
They will not ask for your social security number, and your information is confidential and can’t be shared with anyone outside of the Census Bureau, including law enforcement. If no one is home at the time of the visit, the census enumerator will leave helpful follow-up information to make sure your household is counted.
Remember, this is your chance to make sure Indian Country is accurately counted. Funding for schools, roads, health clinics, and other facilities depends on it. An accurate count may trigger reapportionment, ensuring we are properly represented in Congress. An accurate count gets Tulalip a fair share of grants and other funding; it makes sure your share does not go to neighboring cities or towns. For everyone who is not counted, the Tulalip community could lose approximately $3,000 per person, per year, for the next ten years!
Currently, the Tulalip Census self-response percentage rate is about 10% lower than the rate for Washington State. If you have not already done so, you can avoid having a Census Taker come to your household by responding now online at 2020census.gov, by phone at 844-330-2020, or by mail if you complete and return a Census questionnaire that was mailed to your home.
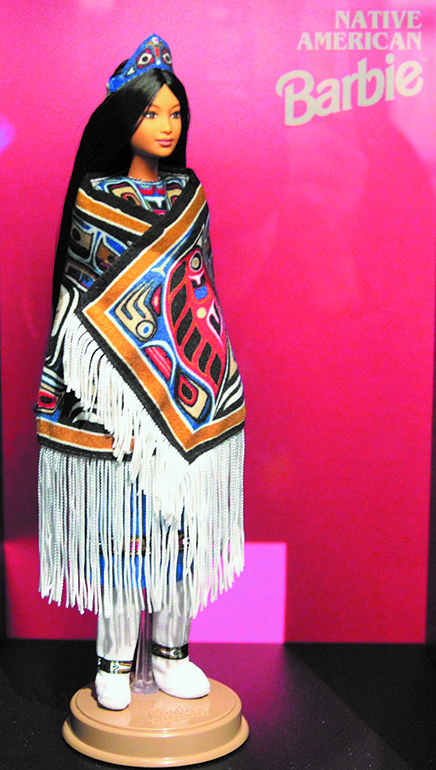

By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
It’s so strange that nearly all that can be named or sold has at some point been named or sold with an Indian word or image. If this seems normal, that’s because it has become normal. It started before the United States was colonized and continues today.
American Indian images are everywhere. From consumer products to Hollywood big screens to local high school, collegiate, and professional athletics mascots. American Indian names are everywhere too, from state (e.g. Alaska, Dakotas, Oklahoma), city (e.g. Seattle, Tacoma, Snohomish) and street names to the Tomahawk missile. And familiar historical events such as Pocahontas’s life, the Trail of Tears, and the Battle of Little Bighorn remain popular reference points in everyday conversation.
Americans, a major exhibition at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of the American Indian, highlights the ways in which American Indians have been part of the nation’s identity since time immemorial. It delves into the power of story, surrounds visitors with images, and invites them to begin a conversation about why this phenomenon exists.
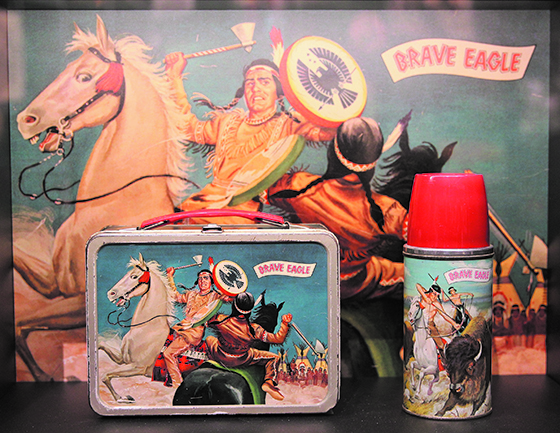

The images accompanying this article are worth a closer look. What if they are not trivial? What if they are instead symbols of great power? What if the stories they tell reveal a buried history and a country forever fascinated, conflicted, and shaped by its relationship with American Indians? Pervasive, powerful, at times demeaning, the images, names, and stories reveal how we have been embedded in unexpected ways in the history, pop culture, and identity of the United States.
As American Indians, we are estimated to comprise just 1% of the entire U.S. population. Yet everywhere you go in the United States, you can see images of us. Why?
How is that Indians can be so present and so absent in American life? One reason is that the land of the free and home of the brave is still trying to come to grips with centuries of wildly mixed feelings about us. Are we the merciless Indian savages described in the Declaration of Independence or are we the noble Indians who strive to be stewards of the Earth? Domestic dependents granted special privileges by the U.S. government or sovereign nations free to govern ourselves? The answer to both questions is somewhere between nether and both.

We have been seen as both authentic and threatening, almost mythological yet deeply appealing. In present day America, citizens of all cultural backgrounds can surround themselves with dream catchers, have Pendleton accessories, and describe a football game as a trail of tears because they know that Indians are in the country’s DNA. They know we have shaped this nation from the beginning and have convinced themselves that the best way to honor us is by filling the void left by cultural genocide with cultural appropriation.
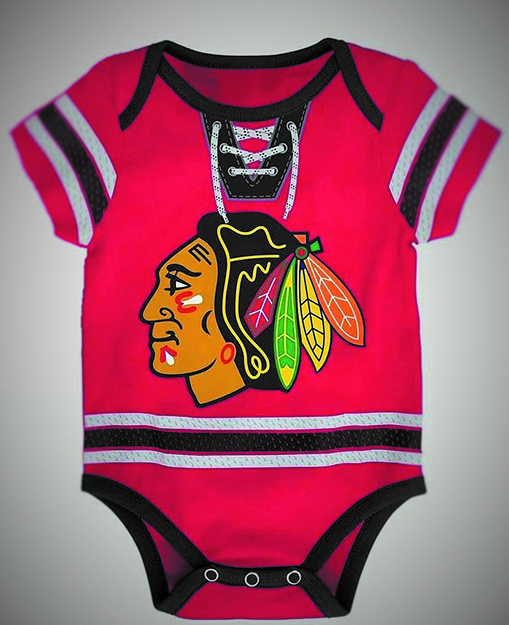

The objects, images, and stories shown here are not just what they seem to be at the surface level. They are insistent reminders of larger truths and an empathic refusal to forget our shared history.


By Kalvin Valdillez, Tulalip News
When the Tulalip Tribes issued their Stay Home, Stay Safe mandate and the governmental entity placed many of its programs on hold and staff on furlough, due to the coronavirus, the Diabetes Care and Prevention program was among the few that momentarily halted all services.
“One of the things you hear on the news is about the people who are at high-risk of contracting the virus, and they always mention diabetes,” said Veronica ‘Roni’ Leahy, Diabetes Care and Prevention Program Coordinator. “I started thinking about what was happening with our patients, what they must be going through, how they are feeling. They must be worried and scared.”
Although there has been a general decrease in the total number of Indigenous people diagnosed with the disease over recent years, Native communities still have an alarmingly high amount of people who are diabetics and pre-diabetics in comparison to any other race nationally.
Diabetes, whether Type 1 or Type 2, is a complex disease that unfortunately, due to deviating from our traditional diets and the lack of access to healthy foods, has affected many of our loved ones and altered the way they live. Managing diabetes is not exactly a walk in the park, considering the amount of medication and insulin one must take in order to just eat a meal. If you are a diabetic and miscalculate the amount of insulin you need to take, or eat too much or too little, you can potentially be in life-threating danger if your blood sugar spikes or drops dramatically.
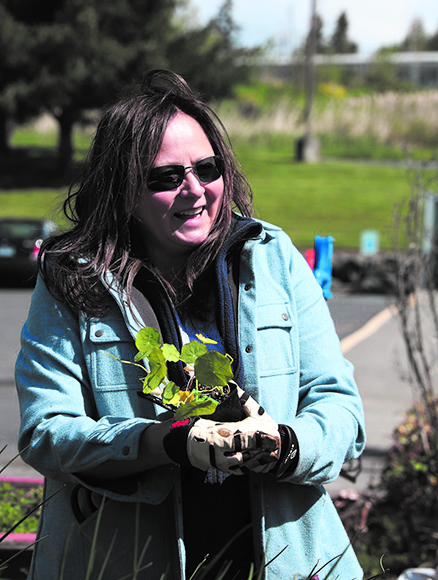

With the health of her patients in mind, Roni pleaded with management at the Tulalip Health Clinic, asking for clearance to come back and figure out a way to reach those patients living with diabetes. Receiving the okay to return, Roni immediately got to work by calling and checking-in on those diabetics who receive care through the program. Able to reach 121 out of 225 patients, Roni asked them a series of questions to get an understanding of how they were doing and what services they required amid the COVID outbreak.
Like many Tribal programs and departments, the Diabetes Care and Prevention program was gearing up for an exciting 2020, aiming to reach more of the community who have been diagnosed with pre-diabetes by planning classes, field trips and a number of fun projects including a fitness expo, complete with exercise workshops and activities, in partnership with Youth Services. With those plans no longer in-play, Roni had to readjust her approach to reach those who needed the program’s resources and services.
“Every month we send the patients a mailer to their homes; something that can provide them with information about COVID,” she explained. “The first one we sent had a thermometer, information on COVID-19 and safety guidelines. This way they know wearing masks are important; we sent them one set and in the next mail-out they’ll get another set of masks.”
In addition to reliable information, Roni is also making sure her patients have the necessary equipment to monitor their health, including blood pressure monitors, thermometers, spirometers and fingertip oximeters, in order to accurately report to their doctors during scheduled telehealth appointments. The program has also been working with other departments within the tribal health clinic that provides services to their diabetic clients. For example, optometry provided Roni with eye health information handouts and eye drops, while the in-house physical therapist offered resistance bands and exercises, so the diabetics can stay active safely from the comforts of their homes.
The mail-out program is a monthly initiative to help those living with diabetes navigate through these corona-times safely. The Diabetes Program also assembles themed-care packages that are sent to their clients quarterly. Last quarter, those diabetics who live on the reservation received a cold care package, filled with immune boosting essentials, at their doorstep. The care packages are hand-delivered by the Diabetes Program Admin Assistant, Brooke Morrison. And for those diabetics who do not live on the reservation, they are able to scoop one up at any time from the health clinic. The next care package will be a naturopathic kit.
During Roni’s telephone assessment, she asks the patient if an emergency situation occurred, do they feel comfortable calling the clinic or the medics, whether it was a diabetic or corona related issue. Many of those patients voiced concern.
“I want them to know that if they have worries or anxieties about calling the office for care because they’re afraid of getting sick, they can call us. A lot of people don’t want to call because they are afraid they’ll have to go to the hospital, and if they go to the hospital their family can’t be with them. That’s part of the conversation I have with them and let them know that you can talk to our nurses, to our clinic and they can help you. Maybe you don’t have to go to the hospital, but you do need to call somebody.”
When reaching out to her patients, Roni quickly learned that a phone call goes a long way. In fact, she recalled numerous phone conversations that resulted in tears. Many of her clients expressed fear about the uncertainty surrounding the coronavirus, as well as loneliness caused by isolation. Roni shared that one gentleman told her that she was actually the first person to call and check on him since the pandemic began.
“We’re keeping really busy with diabetes education that keeps people active and on track with social distancing and keeping things sanitized. Our biggest concern is their safety and we want them to know that we’re here for them,” Roni expressed. “When it comes to diabetic care, sometimes it can be a lonely walk and filled with a lot of uncertainty. We want them to understand that they’re not alone. The mail-out program is a great way to keep interacting with our patients. One of the things people enjoy about our classes is that connection of being together as a group, so we still need to keep those relationships alive and growing and we do that by making sure they have everything they need at home.”
For more information, please contact the Tulalip Diabetes Care and Prevention Program at (360) 716-5641.

Please use the following link to download the August 1, 2020 issue of the syəcəb


By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News

In the ancestral language of this land, Lushootseed, the phrase sgʷi gʷi ?altxʷ means House of Welcome. More than just a name, the Longhouse Education and Cultural Center at Evergreen State College in Olympia being officially dubbed sgʷi gʷi ?altxʷ gives credence to a reciprocal relationship that is both open hearted and open minded.
Created in 1995 as a public service center, the Longhouse’s mission is to promote Indigenous arts and cultures through education, cultural preservation, creative expression, and economic development.
In the beginning, the cultural center’s focus was on six local Puget Sound tribes and their ever-evolving artists. Today, the Longhouse collaborates with highly talented Indigenous artists throughout the Pacific Northwest region, across the nation, and distant lands spanning the globe. Through residency programs with master artists, culture bearers are inspired to develop their abilities while expanding their imaginative capacities in pursuit of creating entirely new boundaries for what defines ‘traditional’ and ‘contemporary’ designs.
“Art allows us to sing without a song, to give our true spirit into something we create out of something nature has given us,” explained Master artist Bruce Subiyay Miller (Skokomish). “Our people create with the natural elements of wood, plant fibers or native plants. Through these acts of creation, our culture continues to live today. That is important at a time when many of us have lost our languages, our customs, and many of the things we look upon as comprising a complete culture.
“We still have our artwork!” he added. “Through that, all the ancestors that lived on this Earth from the beginning of time in our tribal lineages, still exist as long as we have the art. That is what art means to me.”
To celebrate the House of Welcome’s 25 years of groundbreaking work we examine an art exhibition that truly captures the essence of what it means to facilitate cross cultural exchange. Building Upon the Past, Visioning Into the Future showcases cultural concepts and next level skillfulness from over 70 Indigenous artists with whom the Longhouse has built relationship, from the early days, right up to the present. Many of the featured artists have received a grant, taught a workshop, exhibited work, been an artist-in-residence, or otherwise participated in Longhouse programming.
Curated by Longhouse staff members Erin Genia (Sisseton-Wahpeton Oyate) and Linly Logan (Seneca), this one-of-a-kind exhibition features beautiful artistry from tribal members that call this land home. Local tribal representation include Squaxin Island, Skokomish, Puyallup and many other Coast Salish tribes. Tribes from across the nation are also represented, from Alaska to the Great Plains, and across the Pacific Rim, including Native Hawaiians and Maori artists from New Zealand.

“This exhibition reflects the [twenty-five years] of building relationships with artists locally, regionally, nationally and internationally,” stated exhibition co-curator Erin Genia. “Each of the artists you see here in the show has in some way worked with the Longhouse through one of our programs. Native artists are using so many different methods for expressing themselves and we really wanted to display as many of those methods as possible. The result is we have close to ninety beautiful pieces of art, treasures really, that make up this exhibition.”
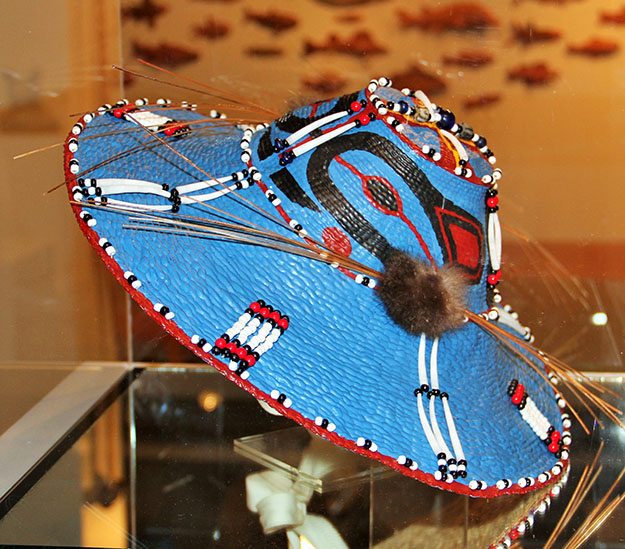

The subjects and techniques exhibited by the Longhouse artists draw from a diverse range of stylistic traditions, which arise from cultural teachings, ancestral lineages, and each artist’s unique experience as Indigenous peoples. Works on display include paintings, drums, carvings, beadwork, photography, baskets, and jewelry.
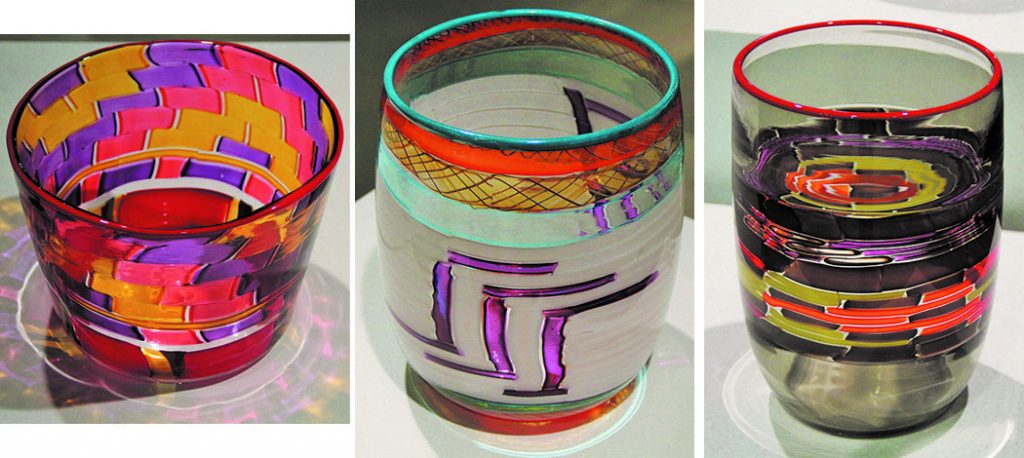
Glass vessels created using basket designs demonstrate the way traditional design can beautifully translate into new media. Other sculptural forms created in clay, bronze and wood, alongside two-dimensional prints, paintings and drawing spotlight the mastery of mediums that Longhouse artists are fluent in.
“As a curator of this exhibition it’s such an awe-inspiring experience to hear from the artists themselves as to the perspective and inspiration behind their artwork,” added fellow co-curator Linly Logan. “We have artists who are very traditional and roots oriented; artists who use the natural resources around them to showcase their creativeness.
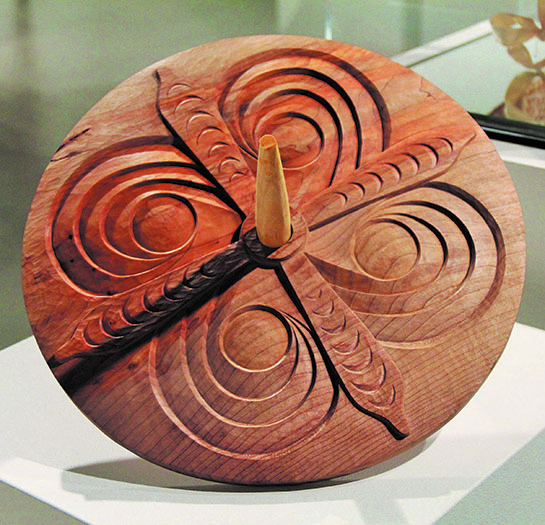

“As Native and Indigenous people we’ve always used the resources around us,” he continued. “In a contemporary lifestyle in nature, we’ve continued to use the resources around us which now include materials other than natural materials. We’ve come full circle in our intent to build upon the past and vision into the future creatively and intellectually as Indigenous people.”
The House of Welcome graciously allowed Tulalip News staff a private tour of the exhibition so that we could share a glimpse of the amazingly creative and exceptional Native art with our local community. These artists are luminaries of their cultures, lighting the pathway back into the far reaches of history, and leading the way into the future with their creative vision.
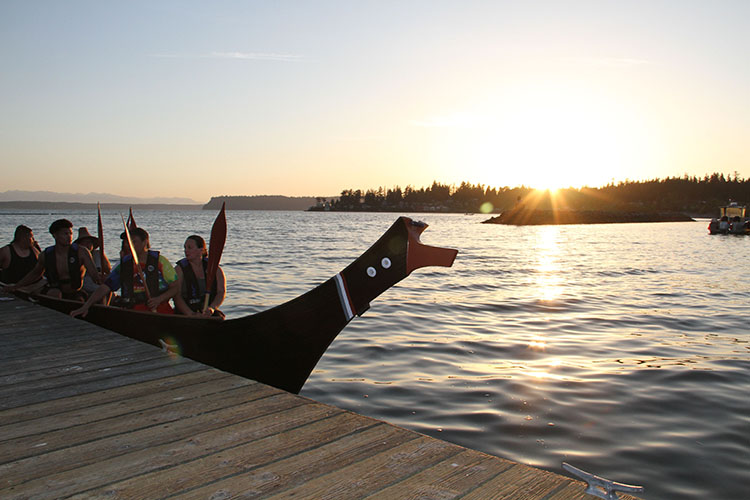

By Kalvin Valdillez, Tulalip News
“The first time I got out on the canoe and went outside of Tulalip Bay, I felt a deep connection not only with the water, but with the canoe,” expressed Tulalip tribal member and Canoe Puller, Monie Ordonia. “I felt my ancestor’s gratitude for me being on the water, the silence of serenity is palpable. It was like an interconnection meditation for me. Every time my paddle digs into the water, it’s like a prayer for my people, the community, and for the water with all that live in it.”
The people of the Northwest have been enjoying beautiful sunrays during the late weeks of July. Although safely partaking in outdoor adventures may be a bit more challenging with the threat of contracting the coronavirus, many people are still finding ways to safely soak up some sun such as family bike rides, scenic car trips, or lounging out on the patio. It’s safe to say the sunshine has brightened up spirits across local Native tribes during a dark time period. And although it’s understandable that we all must make necessary adjustments to protect ourselves and our people, many can’t help but miss the yearly summertime journey across the Salish Sea.
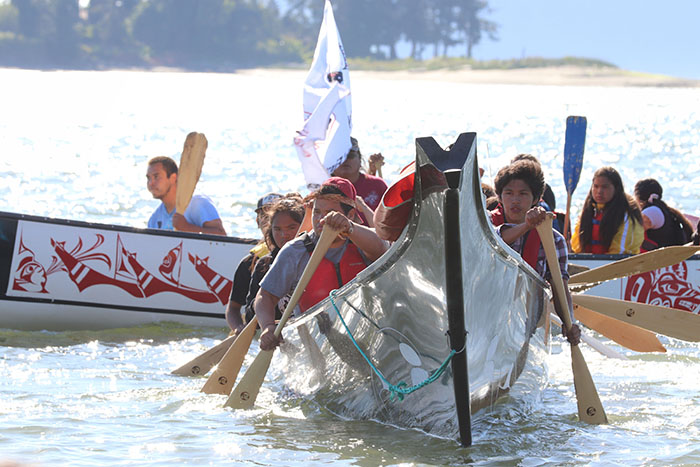

“It was one of those things that was hard to believe,” expressed Tulalip Canoe Family Skipper, Andrew Gobin. “We were getting our canoes ready, we set the practice schedule and we were all planned for journey. We we’re ready to go and all this happened.”
If it were not for the coronavirus, many Natives would be in a cedar dugout canoe this very moment, coasting through the Salish waters and pulling in unison with their canoe family, perhaps offering a traditional song to the sea while enroute to Nanaimo B.C., visiting with different tribes and creating lifelong friendships along the way.
During a colonial celebration, Washington State’s 100th centennial in 1989, Quinault tribal member Emmett Oliver organized an historic moment-in-time, famously known as the ‘Paddle to Seattle’, by calling upon a number of fellow Northwest Treaty Tribes and First Nations bands to participate in a traditional canoe pull into Elliot Bay.
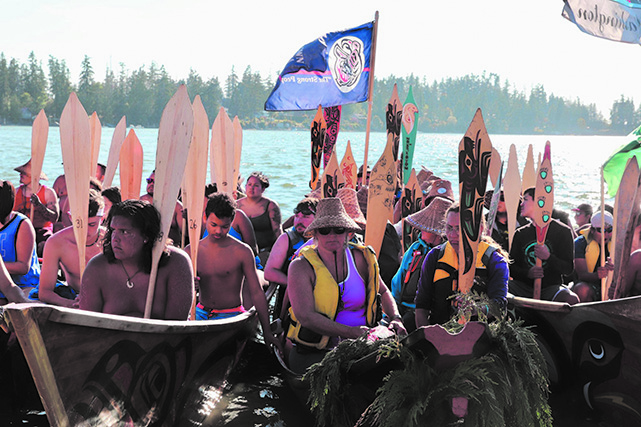

The Paddle to Seattle sparked a cultural revitalization. Once experiencing the medicine offered by the sacred waters, as well as feeling the power of unity amongst coastal Nations, tribal leaders planned the first Tribal Canoe Journey in 1993 with the paddle to Bella Bella. And each summer since, Canoe Journey has been hosted at different villages, helping tribal members reconnect with both their people and ancestral lifeways, while also providing its participants with a lifetime’s worth of memories and healing.
“The first time I did Canoe Journey, there were only ten pullers with our Skipper,” Monie reflected. “No relief pullers, and we didn’t use our support boat to tow us at any time. It was just us pulling to Swinomish. It was a long 10+ hour pull. We were making our final turn to pull up the river to land on Swinomish grounds, we started singing a tribal song and an energy of renewal just came over all of us. We were pulling strong and hard. As soon as we got near the bridge that takes you onto Swinomish land, I became very emotional.
“I couldn’t sing anymore and my eyes were full of tears,” she continued. “My sister Muffy had been the only one of my family who ever done canoe pulling, and she had just passed away in December of 2015. She was the one who inspired me to pull canoe. My grandmother Dora Hilliare Wyakes is buried in Swinomish, so to see that we were pulling up to the bridge that leads to the cemetery where my grandmother was laid to rest, it made me feel like I was honoring both my grandmother and my sister Muffy.”
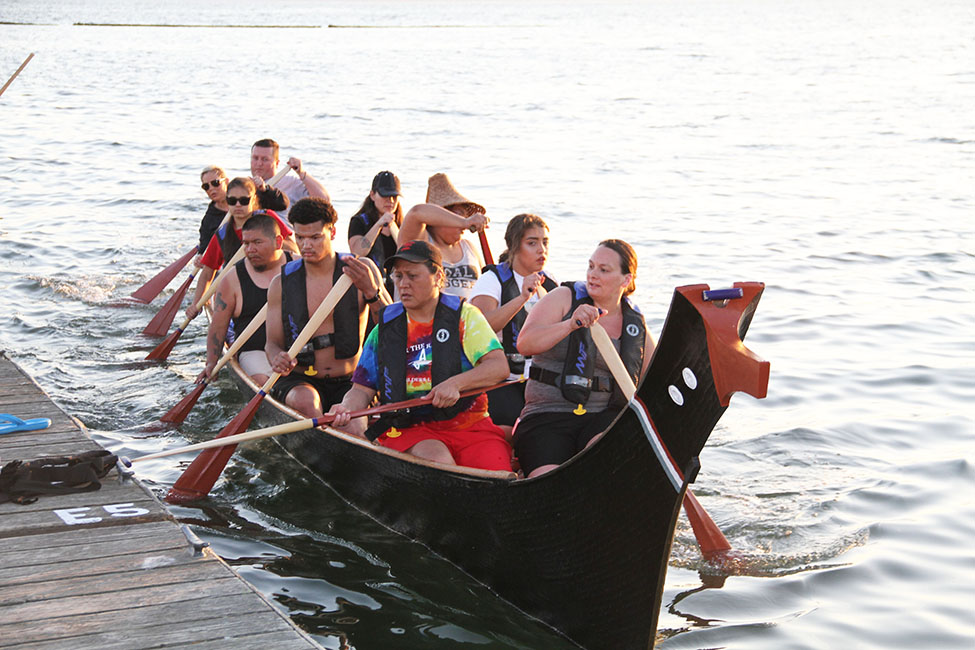

From ’93 until present day there have only been two instances when the Tribal Canoe Journey celebration did not occur, a hiatus in 2015 after no Tribal Nation volunteered for hosting duties, though several tribes did hold small gatherings that year, allowing the canoes the opportunity to still travel the waters. The second instance is this year.
“Before our Tribe even closed, Nanaimo already canceled journey,” explained Andrew. “I thought, like a lot of people, that COVID was just going to be a lot of hype and that it would pass. I was a strong proponent of keeping plans in place and coming up with secondary plans in case journey started up again.”
For Tulalip, Canoe Journey season begins long before their canoes leave the Tulalip Bay shores and extend far past the last song at protocol. In fact, many tribal members dedicate their time months in advance, preparing for journey by harvesting traditional plants and making salves, oils, balms and herbal blends to gift to other tribes during the near month-long experience. The canoe journey participants also take time to practice their traditional songs and dances so when it’s Tulalip’s turn at protocol, their voices are strong and each dance precise, providing medicine while proudly representing the sduhubš way of life.
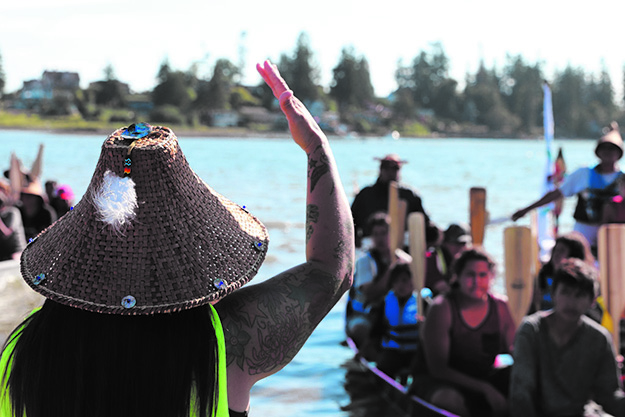

With the absence of this year’s event, many Tulalip canoe family members continued with the work that goes into preparing for journey by harvesting traditional plants and foods within their households and gifting those medicines to local elders as opposed to neighboring tribes. Tulalip singers, dancers and pullers are also staying connected via social media, sharing songs, updates and stories online. Andrew extended his many thanks to the crew who have taken it upon themselves to give back to the community such as Thomas Williams and Dean Pablo.
“I see a lot of people from the canoe family gathering, using this time to harvest, taking advantage of slowing down and taking part in those traditional practices,” Andrew said. “Some of the people on Canoe Journey are turning back to fishing as way to feed their family and their community. People are smoking fish and giving it to our elders. And some of the younger ones are using social media to stay connected this year. The gifts of our people are coming back into the community during this time. When we prepare for Canoe Journey we gather those things and we give them out when we travel. Since we can’t travel, people are taking it on themselves to put it back in their own community.”
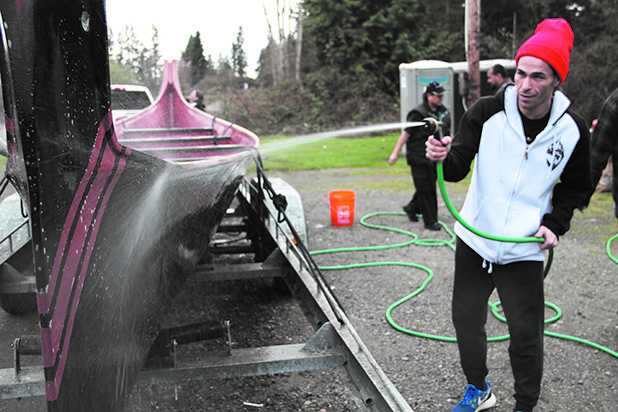
Another tradition of the canoe family is a ceremony that takes place at the beginning of Spring where they formally wake the family canoes, Big Brother and Big Sister, by cleansing and singing songs in their honor, as the canoes are living spirits that come from sacred cedar. The canoes are then taken out on the water twice-a-week until Canoe Journey in order to build up the endurance of the canoes and its pullers.
“I really enjoy practice,” Monie stated. “Getting out on the water as well as the comradery that goes with it. When you practice with mostly the same people every week, they truly become your canoe family. You pull together and sing songs. You encourage each other, so when journey actually begins there is a sense of teamwork, because not one person can pull the canoe by themselves. There is something about sharing your energy on the water in the sacred canoe.”
Though the annual summertime paddle offers healing in many ways, whether it’s pulling on the water, camping and visiting with people from other tribes, or proudly representing your Nation during protocol, many will agree that coming together as a people and forging bonds based on Indigenous culture is one, if not thee, most important aspects of Tribal Canoe Journeys.
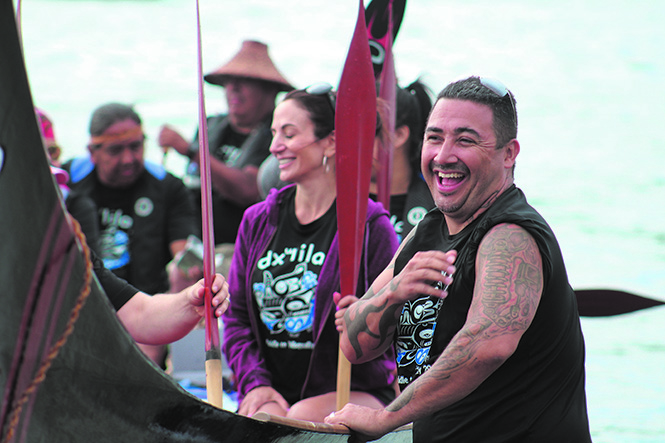

“My favorite part of the journey is that togetherness,” said Andrew. “When we leave Tulalip and travel, we all help each other. We don’t leave anybody behind. If someone needs help, everyone is helping. Everyone is looking out for each other and it really reminds us of the best part of our community and what it means to come together.
“The time on the water, every day is a different adventure. It could be the same crew, same canoe, same paddle, but there’s different jokes and things that happen. Last year, one of the canoes jumped a wave, now those people who were on that canoe all joke about that, they have that unique story they get to reflect on. It’s all about building that community trust and accountability. When we camp and hold circle, everyone is equal, everyone is accountable, everyone has the same responsibilities. Big Shot (Cyrus James) would say, to uphold one another, to care for one another.”
Recently, Nanaimo officially passed the torch to the Tla’amin Nation who plans on hosting the 2021 Canoe Journey festivities in their homeland of Powell River B.C. For more updates, be sure to follow the ‘Tribal Canoe Journeys’ and the ‘Tulalip Canoes’ Facebook pages.