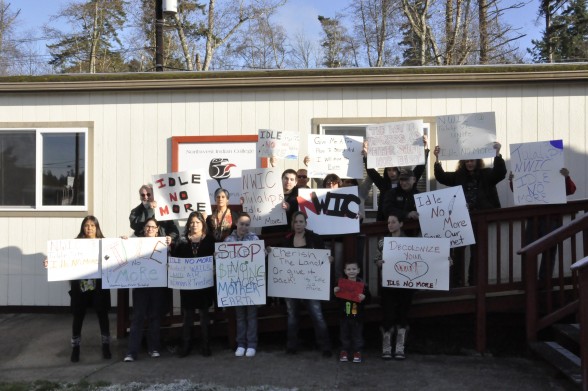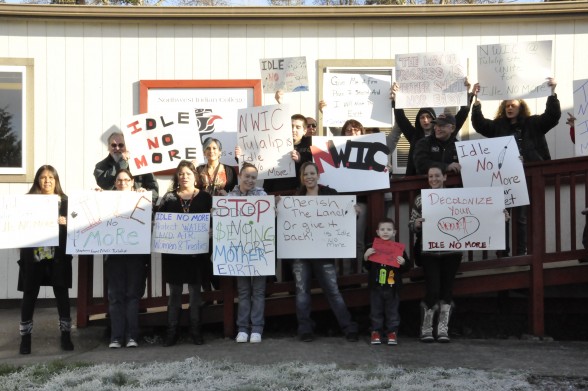By Monica Brown, Tulalip Tribes Communications Department
News Release
Release No. 0354.12
Contact:
USDA Office of Communications (202) 720-4623
Departments of Agriculture, Defense, Energy, and Interior Sign Memorandum to Collaborate to Protect Indian Sacred Sites
Advisory Council on Historic Preservation Also Participates
WASHINGTON, Dec. 6, 2012—Four cabinet-level departments joined the Advisory Council on Historic Preservation today in signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to improve the protection of Indian sacred sites. The MOU also calls for improving tribal access to the sites. It was signed by cabinet secretaries from the U.S. Departments of Agriculture, Defense, Energy and Interior. It was also signed by the chairman of the Advisory Council on Historic Preservation.
“The President is insistent that these Sacred Sites be protected and preserved: treated with dignity and respect. That is also my commitment as Secretary of USDA,” said Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack. “I know my fellow Secretaries share in this commitment. We understand the importance of these sites and will do our best to make sure they are protected and respected.”
“American Indian service members are fighting to protect America on distant battlefields,” said Defense Secretary Leon Panetta. “I’m pleased this new agreement will help protect Indian sacred sites here at home.”
“Protecting America’s air and water and our nation’s heritage is an important part of the Energy Department’s commitment to Tribal Nations across the country, particularly those that are neighbors to the Department’s National Laboratories, sites and facilities,” said Energy Secretary Steven Chu. “I look forward to continuing this important work and collaborating with other federal agencies and Tribal Nations to protect Indian sacred sites throughout the United States.”
“We have a special, shared responsibility to respect and foster American Indian and Alaska Native cultural and religious heritage, and today’s agreement recognizes that important role,” said Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar. “Inter-agency cooperation fosters our nation-to-nation relationship with tribes, and that’s certainly true when it comes to identifying and avoiding impacts to the sites that tribes hold sacred.”
“Through collaboration and consultation, the signatory agencies will work to raise awareness about Indian sacred sites and the importance of maintaining their integrity. The tools to be developed under this MOU will help agencies meet their Section 106 responsibilities,” said Milford Wayne Donaldson, FAIA, ACHP chairman. “The Advisory Council on Historic Preservation is very pleased to be part of this historic initiative to address the protection and preservation of Indian sacred sites.”
The MOU will be in effect for five years and requires participating agencies to determine inter-agency measures to protect sacred sites. It also sets up a framework for consultation with tribes, creation of a training program for federal employees to provide educational opportunities concerning legal protections and limitations related to protection of the sites, creation of a website that includes links to federal agency responsibilities regarding sacred sites and the establishment of management practices that could include collaborative stewardship of those sites.
The MOU calls for development of guidance for management and treatment of sacred sites including creation of sample tribal-agency agreements. It sets up a public outreach plan to maintain, protect and preserve the sites, and calls for identification of impediments to federal-level protection of the sites. Additionally, the MOU provides for outreach to non-federal partners, tribal capacity-building efforts and it establishes a working group to implement the terms of the agreement.
Source: http://usda.gov/wps/portal/usda/usdahome?contentid=2012/12/0354.xml&contentidonly=true
#
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. To file a complaint of discrimination, write to USDA, Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, S.W., Stop 9410, Washington, DC 20250-9410, or call toll-free at (866) 632-9992 (English) or (800) 877-8339 (TDD) or (866) 377-8642 (English Federal-relay) or (800) 845-6136 (Spanish Federal-relay).