By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
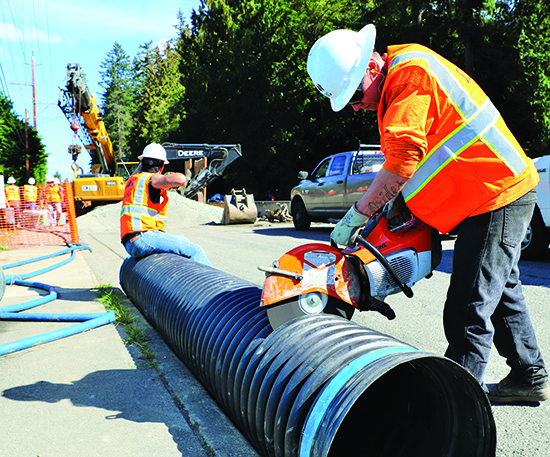
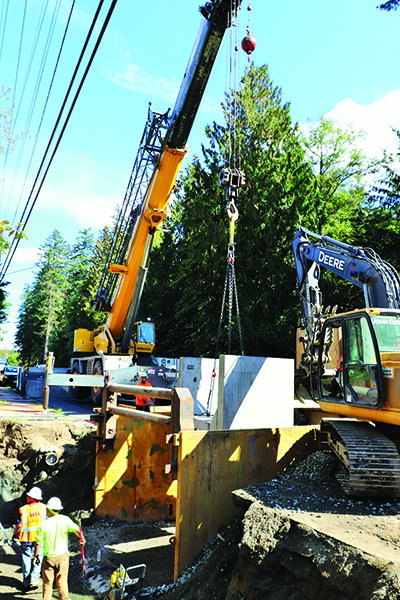
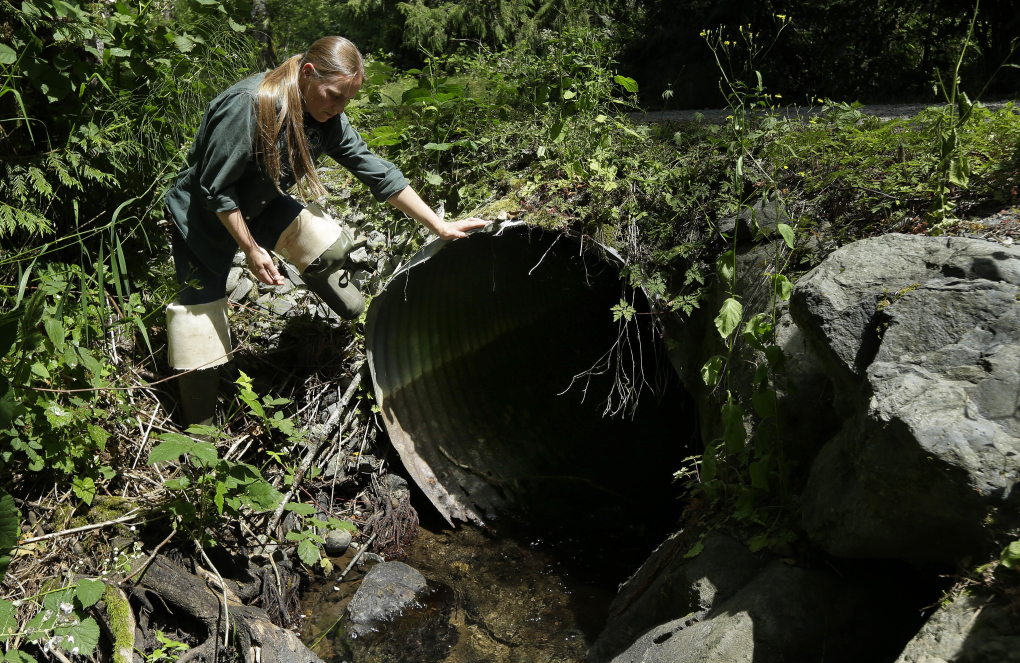
Salmon habitat restoration, honoring treaty rights, and tribal members showcasing successful employment within the construction trades are themes currently in action at an on-reservation construction project. Heavy construction equipment has owned Marine Drive between 19th Ave NE and 23rd Ave NE since September 10, while Snohomish County Public Works replaces a poorly conditioned culvert with one that is fish-friendly by design.
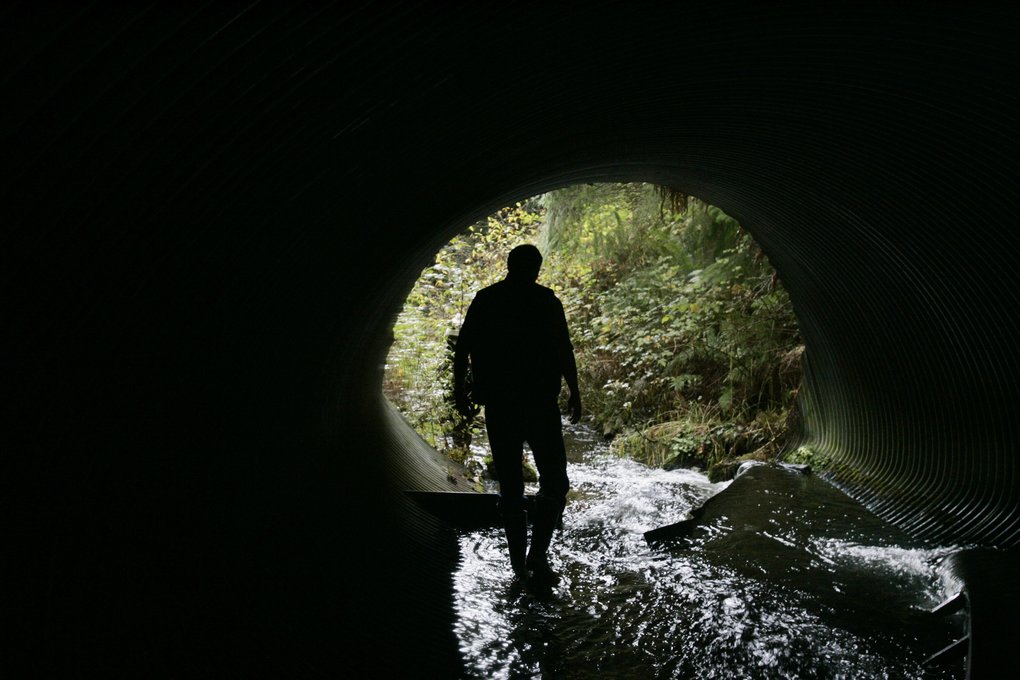
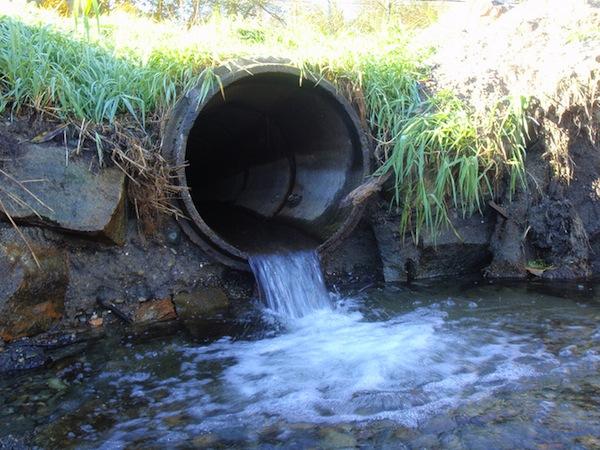
A culvert is basically an underground pipe that allows water to pass beneath roads and other obstructions. The Marine Drive culvert carries water flow from Hibulb Creek to the Snohomish River estuary, which is a fish bearing stream.
According to Snohomish County officials, the existing 24-inch corrugated metal culvert under Marine Drive is in poor condition and undersized. The current culvert is a fish barrier, while the new larger box culvert will meet fish passage requirements.
“Originally engineers designed road crossing culverts to maximize the capacity to carry water with the smallest possible pipe size. This was efficient and economical,” stated Snohomish County representatives. “A fish-friendly design approach is a culvert wide enough and sloped properly to allow the stream channel to act naturally.”
On June 11 of this year, the Supreme Court split a decision resulting in the enforcement of a lower court order requiring Washington State to pay for the removal of over 900 culverts that have become clogged or degraded to the point of blocking salmon migration.
It was a decision that had been passing through the courts for 17 years. The U.S. government sued Washington back in 2001, on behalf of 21 Northwest tribes, to force the state to replace culverts blocking fish passage with structures that allow fish to pass through. Because the pipe-like culverts block salmon from reaching their spawning grounds, they deprive the tribes of fishing rights guaranteed by treaty.
“The Supreme Court has made clear that the treaties promised tribes there would always be salmon to harvest, and that the State has a duty to protect those fish and their habitat,” said Lorraine Loomis (Swinomish), chair of the Northwest Indian Fisheries Commission. “The ruling will open hundreds of miles of high quality salmon habitat that will produce hundreds of thousands more salmon annually for harvest by everyone.”
Snohomish County officials also point out, “The ability of salmon and steelhead to swim upstream to their traditional spawning grounds, while allowing juvenile salmon to move upstream and downstream unimpeded for rearing is vital to their recovery across Washington.”
This specific culvert replacement is vital to salmon recovery and habitat restoration on the Tulalip Reservation, and it’s of particular significance to three TERO Vocational Training Center (TVTC) graduates who are part of the construction team.

Jess Fryberg (Tulalip), Brando Jones (Tulalip) and Jay Davis (Sioux/Turtle Mountain Chippewa) all trained in the construction trades at TVTC and graduated with hopes of pursuing a career pathway that was previously unavailable. Now, each is earning prevailing wages and gaining lifelong skills while working on a project beneficial to protecting treaty rights and salmon recovery.
“Construction has opened up a variety of work for me and each site I’ve worked on teaches me something new,” shared Jess, a 24-year-old tribal member. “Working on this culvert project on the Rez has been a great opportunity. Plus, a long time down the road I’ll be able to tell my kids I helped build it.”
For 27-year-old, single father Brando Jones, he moved from Tacoma to Tulalip two years ago just to have an opportunity to change his future by attending TVTC classes. It was a big move that is now paying off huge dividends as he won sole custody of his son, Dakota, and is building a solid foundation for a career in the construction trades.
“Being able to work on my own reservation while building a future for me and my son is such a good feeling,” shared Brando. “The fact that this replacement culvert will help salmon and protects our treaty rights is a bonus all on its own.”
The Marine Drive culvert construction is expected to complete in the next few weeks, while its positive impact to local salmon habitat restoration is expected to last generations.