Federal officials heard testimony Thursday in Solvang on proposed changes to the process for Native American tribes to get recognized, a procedure speakers described as expensive, lengthy and burdensome.
July 26, 2013 LompocRecord.com Julian J. Ramos/jramos@lompocrecord.comIn June, the Department of the Interior (DOI) released a draft of potential changes to its Part 83 process for acknowledging certain groups as American Indian tribes granted a government-to-government relationship with the United States.
At the moment, the U.S. has 566 federally recognized tribes, of which 17 have been recognized through Part 83. California has 109 federally recognized Indian tribes with between 70 and 80 seeking federal recognition.
The draft proposal, the subject of two sessions Thursday at Hotel Corque, is meant to give tribes and the public an early opportunity to provide input on potential changes to the Part 83 process.
Proposed revisions are intended to improve transparency, timeliness, efficiency, flexibility and integrity in the acknowledgment process, according to the DOI.
However, critics of the proposed rules are calling them the “Patchak patch,” a reference to Supreme Court decision last year in favor of David Patchak, a Michigan man who challenged the way the government takes land into trust for tribes.
They say the proposed rules are meant to drastically limit the uncertainties created by the Patchak decision by adding administrative barriers for potential litigants and rushing fee-to-trust acquisitions, which removes land from local jurisdiction and makes it part of an Indian reservation, under tribal authority.
Larry Roberts, deputy assistant secretary for Indian Affairs, said the presentation during the afternoon public meeting was the same delivered during the morning tribal consultation session.
The public session Thursday afternoon drew between 60 and 70 attendees, including Solvang Mayor Jim Richardson, in the ballroom of the hotel, which is owned by the Santa Ynez Band of Chumash Indians.
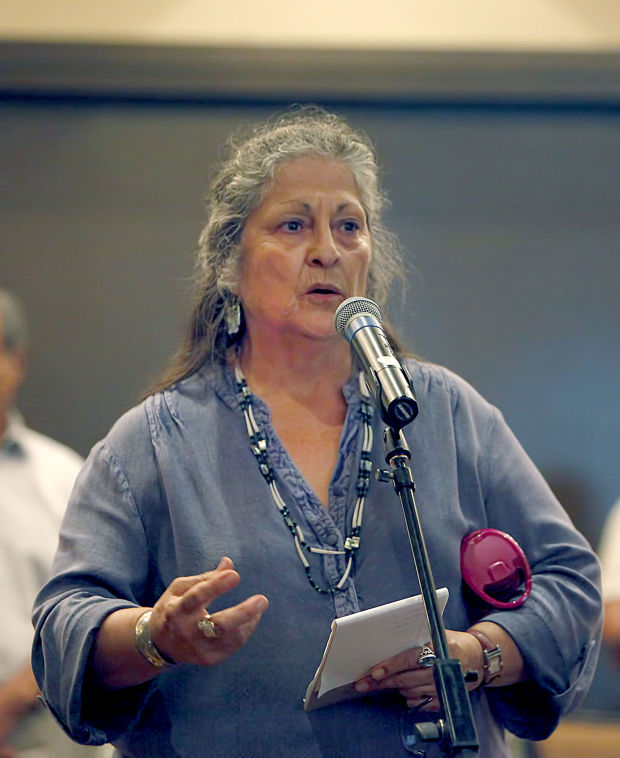

Many of the speakers represented California tribes seeking recognition, a process they described as cumbersome, costly and very time consuming, or as Mona Olivas Tucker, tribal chairwoman of the Yak Tityu Tityu Northern Chumash in San Luis Obispo County, put it, something she doesn’t expect to be completed in her lifetime.
Valentin Lopez, tribal chairman of the Amah Mutsun Tribal Band of Coastanoan/Ohlone Indians in the San Juan Bautista area, said the acknowledgment process is getting more and more difficult, is too lengthy, should be moved out of the hands of the DOI Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) and the burden of proof for recognition should revert to the BIA from tribes.
Michael Cordero, tribal chairman of the Coastal Band of the Chumash Nation, said criteria changes could make it easier to be recognized and tribes, such as his, could benefit from the acknowledgment.
A “Letter of Intent,” which begins the acknowledgment petition process, has been submitted for the tribe, he said.
During a break, Cordero said the session had been helpful in clarifying some issues on the process and requirements.
Across San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara and Ventura counties, the Coastal Band of the Chumash Nation has about 2,500 enrolled members, Cordero said.
Under the proposal, reviews of a petitioner’s community and political authority — criteria for acknowledgment — would “begin with the year 1934 to align with the government’s negation of allotment and assimilation policies and eliminate the requirement that an external entity identify the group as Indian since 1900,” according to the DOI.
No More Slots attorney Jim Marino asked why 1934 is being used in the criteria. He represents several groups against more Indian gaming and land acquisition through the fee-to-trust process, which removes land from local jurisdiction and makes it part of an Indian reservation under tribal authority.
The 1934 Indian Reorganization Act represented a “dramatic” shift in federal policy toward self determination for tribes and the use of that year as a benchmark is meant to reflect that change, Roberts said.
To block attempts to annex property into the Santa Ynez Reservation, opponents of the Santa Ynez Band of Chumash Indians have questioned whether it’s legally a tribal government and thus able to take land into trust via the fee-to-trust process.
The battle centers on Chumash efforts to annex almost 7 acres they own across Highway 246 from the tribe’s Santa Ynez casino.
Members of Preservation of Los Olivos (POLO) and Preservation of Santa Ynez (POSY) have presented documentation to the Bureau of Indian Affairs the groups believe prove the Chumash were not under federal jurisdiction in 1934, and do not qualify to take any land into trust.
By contrast, the Chumash tribe logo and flag says “Federally Recognized Tribe since 1901.”
Due to POLO’s continuing litigation, the group has been advised not to comment on the proposed rule change, POLO president Kathy Cleary said.
Other plans by the Chumash to annex property into the reservation, notably 1,400 acres they own about 2 miles east of the casino and an additional 5.8 acres in the casino area along Highway 246, have also been met with opposition.
Sam Cohen, legal and government affairs specialist for the Chumash, said the proposal is not applicable to the local tribe.
“The Department of the Interior has started to initiate the process of reviewing revisions to the federal acknowledgment regulations for Native American tribes that hope to be federally recognized,” he said in a statement. “Since the Santa Ynez Band of Chumash Indians was federally recognized in 1901, the revisions don’t apply to the Santa Ynez Chumash tribe.”
Transcripts from both sessions will be available at www.bia.gov, officials said.
The discussion draft is available for review at www.bia.gov/whoweare/as-ia/consultation.
Interior officials will accept written comments on the draft until Aug. 16 by email to consultation@bia.gov or by mail to Elizabeth Appel, Office of Regulatory Affairs & Collaborative Action, U.S. Department of the Interior, 1849 C Street, NW, MS 4141, Washington, DC 20240.

